Recommended Blogs
DORA Compliance Roadmap for Europe’s and UK’s Financial Sector

- What is the Digital Operational Resilience ACT (DORA)?
- How will DORA Compliance Impact the Financial Sector?
- DORA Compliance Implementation Checklist
- How will AI Support DORA Implementation?
- How does Tx assist Financial Firms with Compliance Testing?
- Summary
Digital transformation has completely changed the way financial institutes operate. However, with benefits, such as improved CX, data-driven insights, and increased productivity, digital resilience, and security challenges also come with them. According to a survey, organizations that focus on resilience maturity:
- Save $48 million/year on downtime costs
- Are 2.5 times better in adapting to meet recession demands
- Report 2 times greater success rate of their digital transformation projects
- Meet 17% more targets compared to beginners
The UK’s DORA compliance (Digital Operational Resilience Act) aims to upscale financial organizations’ digital resilience. Also, AI plays a critical role in analyzing contracts for DORA compliance, which can benefit organizations.
What is the Digital Operational Resilience ACT (DORA)?
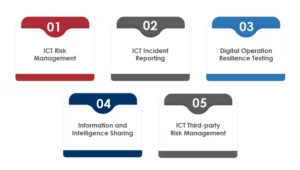
DORA compliance is a European Union regulation that aims to improve digital operational resilience within financial architecture to tackle business disruptions during data breaches or cyberattacks. It will ensure that the financial bodies operating in the EU and the UK remain resilient when the digital ecosystem becomes chaos. DORA focuses on ICT (information and communications technology) and must be followed by all financial institutes in the EU. It covers traditional organizations like investment firms, banks, credit institutions, and insurance companies. The modern entities include crowdfunding platforms and crypto firms. The Digital Operational Resilience Act focuses on five core pillars:
- ICT Risk Management: Organizations must have a detailed documented information and communication technology (ICT) risk management framework, including regular testing to ensure operational resilience.
- ICT Incident Reporting: There should be a robust ICT incident management and reporting process for detecting, remediating/resolving, and notifying the ICT-related events.
- Digital Operation Resilience Testing: Financial entities must conduct regular digital operation resilience testing to ensure the reliability of their ICT defence.
- Information and Intelligence Sharing: Financial organizations can share cyber threat information to raise awareness of new threats, threat intelligence, and operational resilience tactics.
- ICT Third-party Risk Management: Cloud service providers (CSPs) listed as a critical category under DORA compliance must comply with regulations.
DORA regulation is meant to create uniformity within digital operational resilience-related rules, which applies to different financial entities and external ICT service providers.
How will DORA Compliance Impact the Financial Sector?
Since digitization started, financial services have become more accessible and efficient. However, it has also brought some serious cyber risks, making industries of all types and sizes vulnerable to economic losses and operational disruption. Considering the financial environment’s interconnected nature, the impact of cyber incidents can easily disrupt cross-border transactional operations.
The EU’s DORA compliance was introduced to address the financial sector’s growing dependency on digital technologies and increased cybercrimes. This new legislation aims to establish a universal framework for handling ICT risk in the financial industry. It will assist in removing gaps, overlaps, and conflicts between varying regulations within Europe and the UK. Also, the shared rules will make it easier for financial organizations to comply and improve their financial system’s resilience infrastructure.
DORA law will support the coordinated approach to cybersecurity to boost the security of the financial ecosystem against digital threats. This will ensure a secure and resilient digital financial market that will elevate the EU’s economic growth while protecting its businesses and citizens.
The EU’s DORA law is in the critical phase of regulatory implementation and is being synched with the member states’ national laws. Financial organizations need to comply with this new regulation by early 2025. Let’s take a close look at the DORA compliance timeline:
| Year | Description |
| 2020 | The EU Commission published the initial draft of the DORA on September 24, 2020, as part of its Digital Finance Package (DFP). |
| 2021/2022 | After analyzing the European Parliament and Council proposal, the co-legislators organized political and technical discussions in Q1 2022. On November 10, 2022, the EU parliament voted in favor of DORA compliance, and then on November 28, 2022, the EU Council adopted the law. |
| 2023 | The DORA Act entered the complete implementation phase in January 2023. The EU Supervisory Authorities (ESAs) also developed the first Regulatory Technical Standards (RTS) and Implementing Technical Standards (ITS). |
| 2024 | ESA defined and issued multiple RTS and ITS to guide financial entities in implementing DORA requirements. |
| 2025 | The financial entities are expected to declare their compliance with DORA by early 2025. |
DORA Compliance Implementation Checklist
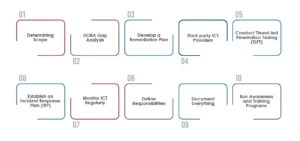
One requires a structured approach to sync with the Digital Operational Resilience Act. Let’s take a quick look at the DORA compliance checklist, which can ensure its successful implementation:
-
Determining Scope:
The first question one should ask themselves is: Do they really need DORA? Check Article 2 to analyze whether your organization falls under DORA’s parameters. Look at factors like business size, service type, and presence in the EU.
-
DORA Gap Analysis:
Analyze and compare your current ICT systems with DORA cybersecurity standards. Conduct the gap analysis to identify the improvement areas and highlight the next course of action.
-
Develop a Remediation Plan:
After identifying the gaps, the next step is to construct a remediation roadmap. Prioritize your methods based on resources and risks, ensuring your plan is achievable.
-
Third-party ICT Providers:
Refer to Article 31 of the DORA compliance requirements to check whether the third-party ICT providers you work with fall under the critical category. You can ensure they comply with DORA and perform due diligence to stay ahead with ongoing monitoring.
-
Conduct Threat-led Penetration Testing (TLPT):
As per Article 26, businesses must implement TLPT by leveraging approved frameworks and running tests on live environments (at least once every two years). This will be part of the stress testing.
-
Establish an Incident Response Plan (IRP):
Set up procedures to manage ICT incidents, which include identifying, tracking, and categorizing issues. Make sure to have a robust communication plan to keep in sync with everyone.
-
Monitor ICT Regularly:
Keep your ICT systems under supervision. Article 8 states that businesses should regularly monitor and analyze risks and constantly update their information assets inventory.
-
Define Responsibilities:
Ensure your members (team, management) handle their responsibilities under Article 5. Remember, top-down buy-in is the key to success here. So, make sure you oversee security policies and digital resilience strategies.
-
Document Everything:
Record everything related to your compliance practices, including incident reporting, risk assessments, test results, etc. Thorough documentation will improve your chances of succeeding in audits.
-
Run Awareness and Training Programs:
Develop employee training and awareness programs to educate employees about cybersecurity risks. The programs should include junior staff and top executives to eliminate knowledge gaps among peers.
How will AI Support DORA Implementation?
DORA compliance must be considered a critical component of a comprehensive framework to upscale digital resilience and ensure compliance. However, DORA implementation significantly challenges businesses to ensure their contracts comply with new regulatory standards. This becomes more challenging when dealing with third-party IT service providers. That’s where AI comes into the picture. DORA and AI can be a great combination to boost security posture. DORA compliance contract analysis automation involves the following process:
|
Extract information like liability clauses, SLAs, and data security from contracts using AI tools. |
|
Check clauses for compliance per DORA requirements by applying rules from regulatory requirements. |
|
AI systems identify risks like inadequate security measures and liability agreements that do not comply with DORA. |
|
AI systems help generate reports on the contract’s compliance and necessary recommendations. |
AI offers advanced practices to accurately and efficiently check DORA compliance contracts. Traditional review methods (manual) are time-consuming and error prone. Leveraging AI-based contract review software would allow organizations to utilize LLMs and NLP to automate contract analysis. They can quickly identify clauses relevant to the Digital Operational Resilience Act. AI systems can scan large volumes of contract data within minutes to spot non-compliance risks. These systems can also identify anomalies and patterns which are impossible to detect manually.
How does Tx assist Financial Firms with Compliance Testing?
Tx assures financial entities with compliance testing by ensuring that systems and processes align with regulatory standards. Here’s how our approach works:
-
Regulatory Expertise:
We have deep expertise in compliance mandates like GDPR, PCI, SOX, and other industry-specific regulations. This ensures our client’s applications align with global and local compliance requirements.
-
Test Coverage:
Our experts leverage advanced QA tools and methodologies to validate data security, digital transaction accuracy, and user privacy to meet strict compliance requirements.
-
Automation:
We leverage AI-based tools to automate and improve QA efficiency by identifying compliance gaps faster and more reliably.
-
Customized Test Strategies:
We create customized test cases and strategies to address the regulatory requirements of financial firms, ensuring uninterrupted audits and inspections.
-
Risk Mitigation:
Our risk mitigation strategies help identify, and address non-compliance vulnerabilities so financial firms can avoid penalties and reputational damages.
Summary
The Digital Operational and Resilience Act (DORA) presents complex compliance challenges to the financial sector. However, by following the comprehensive checklist, one can meet the DORA compliance requirements and be well-positioned against any digital incidents. Think of DORA as a safety net against an unpredictable digital ecosystem. Implementing DORA compliance involves steps like gap analysis, remediation planning, and AI-enabled contract analysis for compliance automation. Also, AI is key in improving the efficiency of DORA implementation by identifying risks and ensuring regulatory adherence. By partnering with Tx, you can access advanced automation practices, QA tools, and customized strategies to align your systems with DORA and other global regulations. To know more, contact Tx experts now.
FAQs
DORA compliance ensures operational resilience, reduces cybersecurity risks, and builds trust with partners and clients. It enhances efficiency by streamlining risk management processes and ensures continuity in the face of disruptions.
The five pillars of DORA are ICT risk management, ICT incident reporting, digital operational resilience testing, ICT third-party risk management, and information and intelligence sharing. Together, they ensure financial institutions maintain robust cybersecurity and operational resilience.
Non-compliance with DORA may result in substantial penalties, including fines and corrective actions enforced by financial authorities. For ICT third-party providers, penalties can reach up to 1% of their average daily turnover, applied daily until DORA compliance requirements are fully met.
DORA applies to financial institutes, including banks, insurers, investment firms, and ICT service providers. It ensures these entities maintain robust digital operational resilience to effectively address potential cyber threats and system disruptions.
Discover more
Stay Updated
Subscribe for more info
