- What is Usability Testing?
- Why Is Usability Testing Important?
- What Can be Avoided with Usability Testing?
- Impact of Usability Testing on User Experience (UX)
- Steps to Perform Usability Testing
- Examples of Usability Testing Use Cases
- Top 7 Usability Testing Tools
- Conclusion
- How Can TestingXperts Help with Your Usability Testing Needs
Software testing and quality assurance go a long way in ensuring digital businesses release top-notch products. However, if product testing and QA fails to focus on the end user’s perspective, the result might be devastating. When creating new applications or updating existing ones, it is crucial to ensure that users find it easy and quick to navigate through the application. This is where usability testing comes into the picture and enables product companies to deliver customer-centric digital products.
What is Usability Testing?
Usability or user experience (UX) testing is the process of measuring how easy an application flow or design is to use with a group of testers or real-life users. It usually involves observing users as they attempt to complete tasks and can be done for different types of designs. It is often conducted repeatedly, from early development until a product’s release. A small set of target end-users use an application to expose usability defects.
Whitney Quesenbery, former President of the Usability Professionals’ Association (UXPA), shared the 5 Es of usability testing given below:
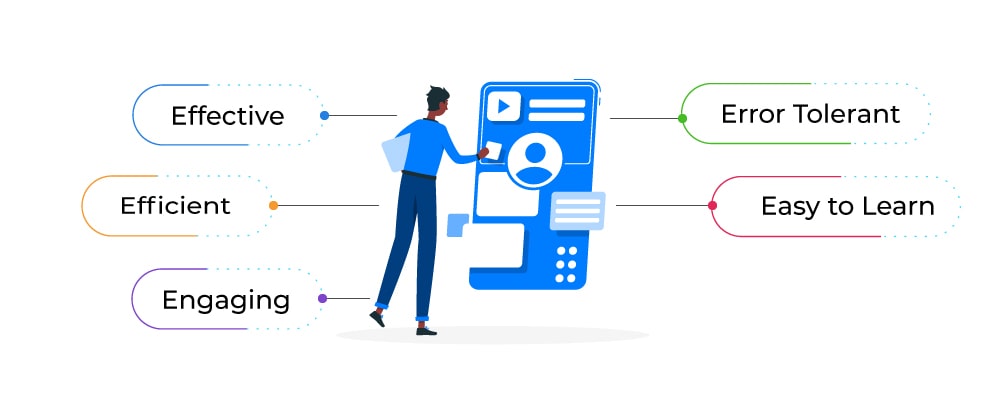
• Effective: How effectively or accurately are the goals achieved
• Efficient: How quickly are the goals met
• Engaging: Is the user interface pleasant and satisfying to use
• Error Tolerant: How well the product prevents errors and can help users recover from their mistakes
• Easy to Learn: How well the product supports initial orientation and continued learning
Usability testing mainly focuses on ease of usage, the flexibility of application to handle controls, and the ability to meet its objectives. Given the benefits of usability testing, it is essential to perform usability testing as a part of the product development lifecycle.
Why Is Usability Testing Important?

One of the critical reasons why testing the application’s usability is essential is that there are many similar applications to choose from. Users nowadays simply move to other applications if they cannot figure out how to use or navigate them quickly.
Usability testing aims at gathering as much feedback as possible on how real users interact with the application as early as possible and as often as possible. This enables product businesses to identify design issues before the application reaches the final build. If usability testing is left until the final build, further changes take more time and effort. Easy-to-use apps and websites increase user satisfaction, whereas apps that are not at par with the usability conventions confuse the users and result in revenue losses for the respective businesses.
App/website usability testing enables enterprises to:
• Measure users’ satisfaction with the application’s interface
• Discover the app’s possible weaknesses
• Discover what the users like the best about the app
• Perform tests in real-world scenarios
• Validate localization and personalization features
• Ensure cross-platform compatibility
• Ensure network, device, and operating system compatibility
• Receive helpful feedback on how the app can be improved
• Implement the improvements and boost customer retention
• Provide a great UX
What Can be Avoided with Usability Testing?

QA teams should include usability testing as an ongoing process throughout the SDLC. Doing so will enable teams to streamline the application development by understanding how the end users will respond. Here are a few issues that can be taken care of with usability testing:
• Inefficient design layout
• Navigation issues
• Inefficient app performance across platforms and networks
• Ineffective tasks that demand too much user effort
• Poor performance leading to app uninstallation
• Common errors on the page
• Typos, grammar, and spelling errors within the content
• Inconsistent branding
Impact of Usability Testing on User Experience (UX)

Usability testing is a critical process in developing and delivering user-friendly products. Unlike most forms of software testing, real users are involved in performing usability testing along with professional testers. Only through various usability testing methods can the product stakeholders know unbiased opinions regarding the application’s likes, dislikes, struggles, and uniqueness. While testers may run different usability testing methods to test the application’s ease of usage, the process typically involves a real-life user or tester using the application or performing a series of tasks to ensure they are delivered with a great user experience.
Types of usability testing methods:
• Usability lab
• Guerilla tests
• Screen or video recording
• Leverage Usability testing partners
• Contextual inquiry
Steps to Perform Usability Testing
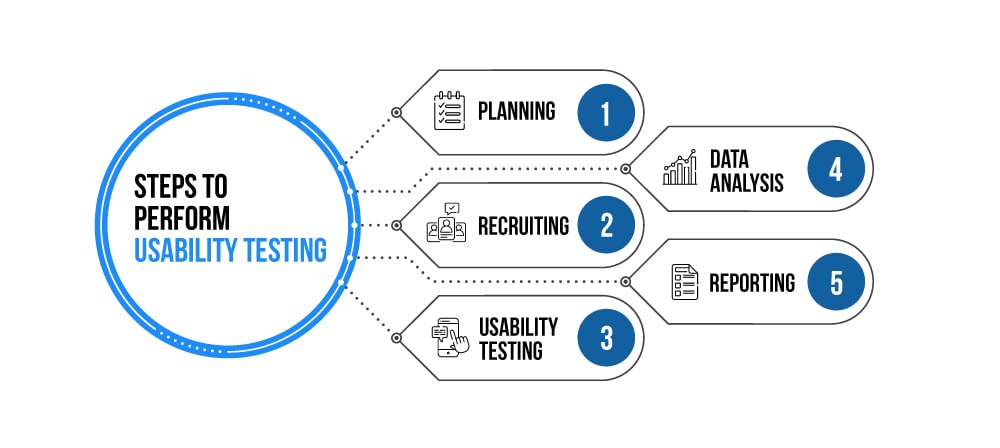
Planning |
The goals of usability test are determined in this stage. Having volunteers sit in front of the application and record their actions is not a goal. QA engineers need to determine the critical functionalities and objectives of the system. Determine the usability testing method, demographics of usability testers, test report formats, etc. at this step |
Recruiting |
During this phase, the desired number of testers is deployed as per the usability test plan. Testers should be chosen who match the desired demographics (age, sex, etc.) and professional (education, job, etc.) profiles as per specifications |
Usability Testing |
Real users, as well as UX experts, navigate through different application functionalities to test the application’s interface and measure user satisfaction. Moderators may use a variety of methods, such as blink tests or expectancy tests, to get instant feedback from the testers or participants. Crowdsourced testing includes asking critical UX-based feedback-based questionnaires such as: • What made completing this task a good experience? • What do you think of the user interface? • What do you think [feature] is trying to communicate to you? • Did you notice that there was an alternative way to do [X]? Why did you go with option [Y]? • How was the process of making a purchase? |
Data Analysis |
Data collected from usability tests is thoroughly analyzed to leverage meaningful inferences and provide actionable recommendations that may improve the application’s overall usability or user experience. Testers should analyze common traits among participants, such as features that took a long time to complete, errors, and functionalities that users did not enjoy |
Reporting |
The usability testing report declares how the testing was performed and lists the recommendations for enhancements. The report features user ratings on a Likert scale, notes from the feedback sessions, audio & screen recordings, etc. Findings of the usability test are shared with all concerned stakeholders, which can include the designer, developer, client, and even the CEO |
Examples of Usability Testing Use Cases

• Is the system easy to learn?
• Does the application add value to the target audience?
• Are the content, color, icons, and images aesthetically pleasing?
• Are the controls used self-explanatory?
• Is the application responsive on all the targeted devices and operating systems?
• Is the necessary help available for users to understand the application?
• Is the navigation minimal to reach the desired screen?
• Is the scrolling minimum?
• Is the format of screen/pages in the application/website uniform?
Top 7 Usability Testing Tools

| S.no. | Tool | Key Features |
| 1 | CrazyEgg |
• Easy to setup with JavaScript placed on each page • Heatmap records the visitor clicks • Scroll map records how far down users scroll for each webpage • Overlay segregates the number of clicks received on each page • Confetti provides insights on components as well as search items |
| 2 | Userzoom |
• Measure and analyze user experience on websites, apps, and prototypes • Provides details for every stage of the product development lifecycle • Interview users while using the app • Provides critical reports such as click data, user actions, unique views, and heat maps • Provides rapid results and automated reports |
| 3 | Loop11 |
• Enables non-moderated remote usability testing • Data is displayed in reports containing task time, path analysis, etc. • Need not load software on the website • Easy to use and understand and does not require any coding • Can be used on any website and provide real data |
| 4 | Usabilla |
• Collects real-time feedback on the website, phone application, and prototypes • Analyze the data in custom environments by pulling data into the environment • Can include response buttons in content and emails • Enables data visualization in the form of bars, graphs, and pie charts |
| 5 | TryMyUI |
• Provides standalone and customizable tests • Tracks mouse movements and keystrokes and serves the System Usability Scale Questionnaire • Provides advanced filtering, quantitative data, and collaborative analysis |
| 6 | Usability Hub |
• Heatmap shows where people click first on the site, assessing the effectiveness of the link placement • Backroom and chat features for interviews
|
| 7 | UX Tweak |
• Record users with session recording feature Replay Visitors • SmartSearch feature can search the session recordings for specific interactions such as clicks on particular elements or typing in input fields • Conduct a card sorting study using the CardSort feature |
Conclusion
Usability testing is required by all business applications as it gives first-hand information about whether the product meets the user’s expectations. It is very helpful for getting user reactions and feedback about the product.
Leverage TestingXperts usability testing services and gain insights about product experience in advance to ensure its success.
How Can TestingXperts Help with Your Usability Testing Needs

• Talented pool of Usability testing experts to guide you on the strategy
• Assistance in coming up with a list of sample users based on application characteristics, business objectives, and user demographics
• Ability to perform crowdsource testing through the wide user community
• In-depth survey forms that ensure real user usability testing
• Comprehensive usability reports along with detailed recommendations for improvement
Talk to our QA experts today.
Discover more
Get in Touch
Stay Updated
Subscribe for more info