EDI – Electronic Data Interchange. Definition: EDI is a computer-to-computer exchange of business documents in a standard electronic format between business partners without the need for human intervention. EDI permits exchange of multiple business documents, such as purchase orders, shipping notices, invoices and more. It also permits multiple companies across countries to exchange business documents electronically.
Contents
1. What are the types of EDI?
2. What are the common EDI Standards?
3. EDI Benefits for Enterprises
4. Common EDI Testing Challenges
What are the types of EDI?
EDI via VAN: VANs or the Value Added Networks are the private networks in which electronic business documents are exchanged within the partners. Here, the provider manages the network and ensures in providing mailboxes for sending and receiving EDI documents.
Mobile EDI: The traditional methods have made users access EDI by VAN or the Internet to receive and send EDI-based business documents. Mobile EDI is experiencing limited adoption because of security concerns and restrictions available in the mobile devices
EDI via AS2: AS2 is referred to as an internet communication protocol. This enables to transmit data securely on the internet.
Web EDI: In this type, EDI is conducted by using a standard Internet browser. Web EDI helps in making EDI easily available for all organizations that have a limited need for utilizing a service.
Direct EDI: In this type, a single connection is established between two business partners. Direct EDI is also known as point-to-point EDI and it is mostly used in enterprises where daily transactions are more between customers and suppliers.
What are the common EDI Standards?
In order to define a generic and repeatable set of structured data placeholders or rules for creating business documents, there was an establishment made for EDI Standards. In these documents there were a lot of included such as purchase orders, shipment notifications, invoices, in an electronic form. These standards were needed to make the businesses avoid spending more time and resources on regular business documents.
The commonly known EDI standards are:
- GS1 EDI: This standard is used in retail industries globally
- ODETTE: This standard is used by the European automotive industry
- TRADECOMS or GS1 UK: This standard is successful in the Great Britain industry
- HL7 with HIPPA regulation is predominantly used in the US healthcare industries
- ANSI ASC X12 or X12: This EDI standard is used for supply chain, transportation, finance and insurance in North America
- RosettaNet: It is based on XML and it is in industries including manufacturing, service and supply chain
EDI Benefits for Enterprises
EDI is predominately used in large and small companies because of the range of benefits it offers.
Reduces the usage of Paper: The implementation of EDI helps in reducing the usage of paper. This is really a great benefit for the enterprises as this not only results in cost reduction but even helps in reducing the team efforts in writing and prevents the environment from the emission of carbon dioxide.
Increases Business Efficiency: By adopting the EDI methods, enterprises eliminate paper-based tasks and adopt automation. This will minimize human intervention and reduce the chances of human error. Also, this will help the teams to concentrate on higher-level tasks that can yield faster productions. This way of devoting employee’s attention to high-level tasks helps the enterprise to seek more productive and efficient results.
Reduces Cost: Enterprises implementing EDI methods seek most of the cost savings. This is one of the main reasons for many enterprises to choose EDI. EDI helps in adopting automation, increases the response time, limits the occurrence of errors with less paper usage. All of these effectively help in reducing the cost requirements and increase the efficiency of the management system.
Increases Speed and Accuracy: EDI effectively helps in speeding up the business cycles. It helps in increasing the data flows, improves the data quality, helps in delivering faster transactions by eliminating the various challenges such as illegible handwriting, lost emails, etc. Also, the reliability between the businesses even improves with the EDI. The use of EDI helps to overcome the multiplying number errors by eliminating the duplicate data and manual work. In addition, EDI even ensures that the information that is received is accurate and it is meeting the required conditions. This helps in maintaining a good relationship between the trade partners with accurate and speed deliveries.
Enhances the services for End-User: EDI is popularly known as the tool helping enterprises to maintain proper communication with the suppliers and customers. Also, this eliminates the delays or the errors associated with the previous communication and effectively facilitating collaborations and relationships.
Ensures Security: The use of EDI limits the usage of emails as these are prone to get altered. Whereas, EDI use encrypted systems to increase the security of the document during the interchange. Also, EDI ensures processing secured transactions by using a range of security standards and communication protocols.
Among the many best reasons, the impressive cost savings are one of the best benefits the EDI is offering for enterprises. On the other hand, the implementation of EDI has challenges too, especially while testing or validating EDI-based applications. Given the importance of EDI, testing EDI-based applications is considered as ‘impeccable.’ Let’s take a quick view of the number of testing challenges involved during this process.
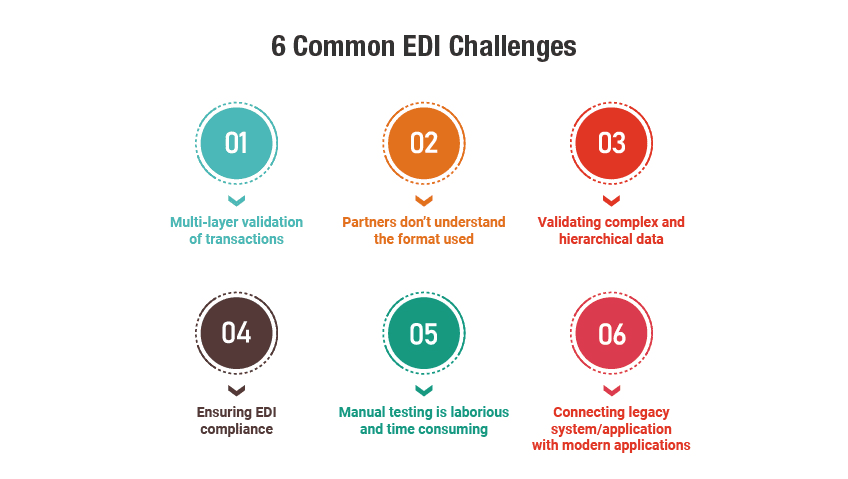
Common EDI Testing Challenegs
Challenge 1: Multi-layer validation of transactions
When testing EDI-based applications, sending each transaction and validating its result manually can be cumbersome and error-prone. This becomes even worse when the testers fail to exercise a wide range of test cases accurately. This often involves managing hierarchical and complex data sets and perform multi-layer testing or validation of each transaction.
Challenge 2: Partners don’t understand the format used
There are numerous file formats in use for EDI-based applications. These formats include: EDIFACT, X12, CSV, AS2, TRADACOMS, and more. Sometimes, the file formats that are used by an enterprise might not be understood by its partners’ systems, or vice versa. In this case, the enterprise or partners need a solution that validates data in various formats, which will be an overwhelming task.
Challenge 3: Validating complex and hierarchical data
The more partners, manufacturers, and suppliers an enterprise coordinates with as a part of its trading, the complexity of the network increases. The enterprise needs to be able to connect to partners’ systems and have to deal with multiple challenges that may arise while validating the information exchange transactions.
Challenge 4: Ensuring EDI compliance
Translating EDI files from one or multiple trading partner’s format to a standard format that is used by the receiver is one of the biggest challenges. Meeting all the trading partner’s EDI requirements is essential for an organization to become EDI compliant.
Challenge 5: Manual testing is laborious and time consuming
EDI-based application testing consumes a lot of man hours as it involves the complex nature of the workflows. EDI based test automation service is needed to help minimize human work, and allow test engineers to focus on test analysis.
Challenge 6: Connecting legacy system/application with modern applications
If an enterprise is using a legacy system or an application, it may host a range of challenges, including:
– Relevant legacy programming skills are required to support the legacy system
– The generated reports from legacy system data, especially that are in various formats are difficult to interpret
It is imperative to understand these challenges and address them with EDI test automation capabilities. Today, only very few companies have full-fledged capability to test EDI-based applications effectively and help businesses gain a competitive edge in the marketplace. TestingXperts is one of them.
Watch this space for the next post in the series, EDI Test Automation & Testing Types.
Discover more
Get in Touch
Stay Updated
Subscribe for more info