Regulatory compliance is crucial for companies to ensure software safety, quality, and privacy. Businesses have started a strategic shift towards a more regulation-centric approach, majorly in finance, eCommerce, insurance, and healthcare. A non-compliant product can cause serious issues like legal actions, data breaches, etc. This could severely affect user trust and brand reputation. But the question is: How can someone ensure the software fulfills functional requirements and regulatory standards?
The complexities involved with regulatory compliance are a sheer volume of processes, documentation, and data. Manual testing, once a primary method that businesses used to ensure compliance, no longer fits in this tech-driven world. It is a time-consuming and error-prone method. As regulatory standards evolve and become more complex, businesses need a more robust, foolproof, and efficient approach. This is where test automation comes in. Let’s examine how test automation helps achieve regulatory compliance for software products.
Understanding Regulatory Compliance Landscape
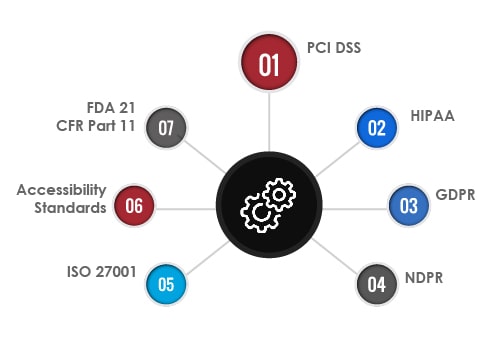
It is now common practice to ensure that software must adhere to multiple regulatory compliances and standards (international or regional). But let’s imagine a scenario where software or mobile applications operate freely without security or regulatory checks and balances. What would be the result? An utter chaos. Multiple frameworks, data compliance, and standards were made to prevent this chaos. Following are some of the well-known compliances:
PCI DSS:
The Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard is necessary for credit/debit card payment software. It covers finance and eCommerce platforms that process, store, or transmit credit card details. This data compliance mandates a set of security measures, such as:
• Strong encryption methods to protect cardholder data against breaches and fraud
• Conducting Regular vulnerability assessments
• Having a secure network architecture
HIPAA:
The Healthcare Insurance Portability and Accountability Act is necessary for managing healthcare data in the USA. It has a set of standards that protect sensitive patient data. Healthcare applications dealing with patient records systems, telemedicine platforms, etc., must ensure that PHI is securely stored, accessed, and shared. Methods like encryption, access controls, and audit trails should be implemented to prevent unauthorized access and breaches.
GDPR:
The General Data Protection Regulation affects businesses dealing with EU resident’s data. It doesn’t matter where the organization is headquartered. If they are doing business with European customers, they must adhere to GDPR compliance. It is a data protection law or data compliance that emphasizes user consent, design privacy, and data minimization. Businesses should ensure their products provide clear privacy notices and allow users to control their data.
NDPR:
The Nigeria Data Protection Regulation sets guidelines for protecting data in Nigeria. It governs personal data collection, processing, storage, and disposal. Software specifically made for Nigerian users must comply with NDPR standards, including obtaining consent, respecting user data rights, and protecting data.
ISO 27001:
This is an international standard for the Information Security Management System (ISMS). It provides the framework for businesses to handle assets security like intellectual property, employee details, financial information, etc. Software following this standard must ensure security controls, continuous improvement, and risk management processes are handling information security.
Accessibility Standards:
Standards like WCAG ensure web content is accessible to people with disabilities. Businesses must ensure their products are operable, understandable, robust, and perceivable for all users (including visual, auditory, cognitive, or motor impairments). It covers keyboard navigation, content presentation, color code, reader compatibility, etc.
FDA 21 CFR Part 11:
This compliance covers pharmaceutical and medical device industries in the USA. It sets the criteria for selecting electronic records and signatures over paper records. Software for these industries must ensure data confidentiality, integrity, and authenticity by implementing secure user authentication, system validations, and audit trails.
Challenges with Manual Testing

Traditionally, businesses relied heavily on manual testing for compliance purposes. In this approach, QA experts execute test cases manually without using automated tools. It was a problematic process, and the need for precision, efficiency, and consistency drew limitations on manual methods. Following are some of the challenges related to manual testing:
Non-compliance Risk due to Human Errors:
Manual testing depends on the tester’s skills and attention to detail. Human errors like mistakenly overlooking a compliance-related defect, inconsistency in testing methods, etc., lead to non-compliance penalties.
Inconsistency in Compliance Validation:
Manual tests yield inconsistent results because of the subjective nature of this type of testing. This inconsistency does not align with regulatory compliance, where standard adherence and consistency are top priorities.
Challenge in Covering Compliance Requirements:
Manual testing covers limited test cases due to resource and time constraints. This results in inadequate coverage of regulatory compliance requirements, especially complex ones.
Difficult to Adapt to Changing Regulations:
Regulatory standards update regularly, requiring quick adaptation in the testing process. Manual testing becomes a hassle, and difficult to keep up with the changes, leading to gaps in compliance.
Compliance Documentation Challenge:
Proper documentation is a key aspect of regulatory compliance. Manual testing lacks the rigorous documentation (detailed test logs and reports) to present compliance.
Resource and Cost Constraints:
Compliance needs repeated and extensive testing. Manual testing is time and labor intensive, increasing the cost and resources required. This makes manual testing less feasible for frequent and thorough compliance checks.
Difficulty in Conducting Regression Testing for Compliance:
Regression testing is necessary whenever there’s a new update or change in software. It ensures that the new updates are in sync with existing compliance standards. Manual testing is a slow and cumbersome task that increases the risk of missing compliance checks, which is unsuitable for regression testing.
Role of Test Automation in Regulatory Compliance
This is where test automation comes into play. It involves using automation tools to execute pre-written test scripts on a software application before releasing it into production. The process is faster, reliable, and can run repeatedly with minimal cost. Following are the ways test automation supports the regulatory compliance process:
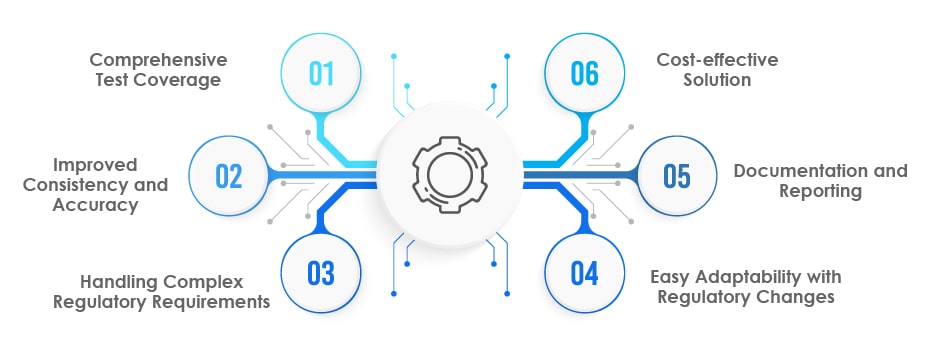
Comprehensive Test Coverage:
Automated tests cover a broader range of test scenarios than manual testing. During software development, it is essential to ensure that it meets all aspects of compliance requirements.
Improved Consistency and Accuracy:
Automation prevents human errors and provides accurate and consistent results. These aspects are crucial for compliance, where a slight deviation in the software’s functionality significantly impacts regulatory standards.
Handling Complex Regulatory Requirements:
Test automation enables efficient handling of complex testing scenarios necessary for compliance. It involves running test cases under varying loads and conditions, which is impossible in manual testing.
Easy Adaptability with Regulatory Changes:
Regulatory standards are dynamic and evolve depending on technology advancements and other scenarios. Updating an automated testing framework based on new regulations is easier than manual methods. It ensures businesses can easily adapt to regulatory changes and avoid penalties or legal issues.
Documentation and Reporting:
Test automation generates detailed documentation of logs and reports necessary for compliance audits. It acts as proof that the software product meets the necessary regulatory requirements.
Cost-effective Solution:
Although initial setup costs may be higher, test automation is more cost-effective in the long run, especially for projects requiring ongoing compliance testing. It also enables continuous compliance monitoring, ensuring the software remains compliant as it evolves.
How to Implement Test Automation for Regulatory Compliance?
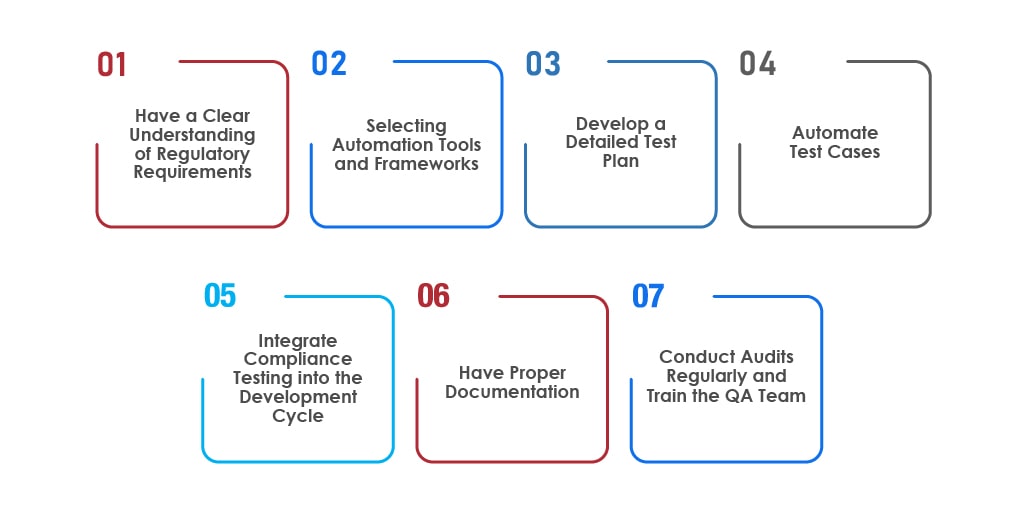
Implementing test automation can benefit any business that wants to ensure its software products meet regulatory compliance and legal standards. It involves a strategic approach focusing on precise and thorough testing to fulfill compliance requirements
Have a Clear Understanding of Regulatory Requirements:
The first step is clearly understanding compliance requirements specific to the software product. The regulations vary from industry to industry, such as HIPAA for healthcare, which governs patient data protection, and GDPR, which protects EU residents’ data. A clear understanding of these guidelines eases the development of focused test cases.
Selecting Automation Tools and Frameworks:
Selecting the right automation tools and frameworks specific to compliance needs is crucial. It should be based on the tool’s ability to perform comprehensive testing, including other tasks like detailed reporting and simulation of test environments. Tools with customization features and the ability to integrate with the development environment can be prioritized.
Develop a Detailed Test Plan:
Have a detailed test plan that covers all compliance aspects. The plan should outline every test case to address multiple compliance requirements. It should have different testing scenarios to cover every aspect of compliance regulations.
Automate Test Cases:
Make sure to automate repetitive and critical test cases that run frequently and are vital for ensuring software complies with specific regulations. Automate regression test cases to ensure new updates or features do not compromise existing standards.
Integrate Compliance Testing into the Development Cycle:
Make compliance testing an integral part of the software development life cycle. This will ensure constant monitoring and maintenance of compliance standards in every phase of the development process.
Have Proper Documentation:
Configure automated tests to generate detailed documentation for audit purposes. It will also serve as evidence of compliance, including comprehensive test logs and reports. Make sure to review and update the test cases regularly to ensure automated testing remains effective in meeting the latest compliance requirements.
Conduct Audits Regularly and Train the QA Team: Make sure to conduct regular compliance audits to review test results and strategies. Also, the adjustments made to improve efficiency and effectiveness of compliance must be verified. Train the QA team in both test automation techniques and compliance requirements. The training will serve as a stepping-stone for implementing automated tests that meet regulatory standards.
Conclusion
Test automation is key to meeting regulatory compliance in the software development life cycle. Organizations can meet all global data compliance and regulatory requirements through effective test automation techniques, such as PCI DSS, HIPAA, GDPR, etc. Automating the process of testing (while at the same time reducing dependence on manual testing) represents a significant step towards maintaining quality and integrity in the fast paced and ever-evolving world of software development. And partnering with a professional QA services provider such as TestingXperts would allow your business to integrate test automation with the regulatory complaint process seamlessly.
How can TestingXperts help with Regulatory Compliance Automation?

At TestingXperts, we understand the importance of compliance testing in software development. By implementing test automation strategies in regulatory compliance, we support businesses in enabling faster delivery of software products. Our years of experience in automation and compliance testing ensure your business meets regulatory standards and excels in its digital endeavour’s.
• We use the latest tools and technologies to deliver precise and efficient testing results, ensuring your software product complies with industry regulations and standards.
• Our experts have extensive knowledge of data compliance and standards across industries. It allows us to provide insightful solutions tailored to your unique business needs.
• We offer customized test automation strategies to speed up the compliance auditing process. Our compliance framework would seamlessly integrate with your digital business initiatives.
• Our risk management strategies help mitigate compliance issues to ensure adherence to regulations and protect your business from legal and financial repercussions.
To know more, contact our QA experts now.
Discover more
Get in Touch
Stay Updated
Subscribe for more info