When it comes to supply chain management, businesses usually stick with what works for them and avoid implementing new tech advancements. Although most businesses employ innovative solutions like AI, RPA, etc., many still manually complete inventory counts, packing, picking, etc. Some are unaware that the old manual supply chain processes are not feasible in the current digital business age and are detrimental to business success. The gap between applications would cause inefficiencies and a lack of transparency, leading to bottlenecks. This would also increase the risk and cost of supply chain management. With supply chain automation, businesses can improve operations by enabling seamless workflows, real-time reporting, and modern app integration.
Low-code automation software can enable businesses to close software gaps, facilitate agile workflows to gain visibility across operations and improve the efficiency and experience of every stakeholder. Also, with the advancements in internet technology and smartphone accessibility, the requirement for efficient inventory and warehouse management has become more critical. This is reflected in the rapid use of robotics in warehouses, where laborious tasks are taken over by automated systems to ensure operational efficiency and worker safety.
What is Supply Chain Automation?

Supply chain automation uses intelligent technologies, such as digital process automation, RPA, AI, and ML, to streamline processes, improve efficiency, and connect applications within supply chain operations. It changes how products are managed, moved within/across companies, and logistics. Even the logistics automation market is expected to grow at a 12% CAGR by 2032. Intelligent technologies are critical in supply chain automation, from warehousing and inventory management to transportation and delivery. For example, AI/ML helps identify bottlenecks in the supply chain, facilitate better decision-making, and optimize operational efficiency.
Supply chain automation does not replace labor with machines. It creates a more connected, automated, and responsive supply chain. With digital twins and predictive analysis, businesses can simulate and analyze supply chain operations, optimize processes, and enable proactive product management.
Why is Supply Chain Automation Necessary?

Supply chain automation is necessary in the digital business world because of the complexities of dynamic market demands. Following are some of the reasons why businesses should invest in supply chain automation technology:
• It is necessary to meet the requirements of faster delivery and transparency in the order processing.
• It facilitates agility and responsiveness to global supply chain challenges, allowing businesses to address market changes and disruptions.
• Automation helps reduce dependency on manual labor in areas with higher labor costs and labor shortages and improves operational efficiency.
• Technologies like AI, ML, and IoT provide real-time insights for better inventory management, optimizing stock levels, and reducing waste.
• It helps improve risk management and mitigate compliance issues in supply chains with improved tracking and monitoring features.
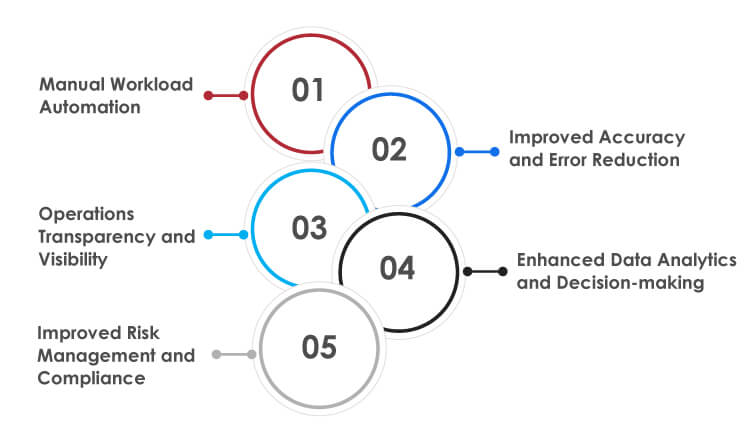
5 Benefits of Supply Chain Automation
Supply chain automation helps improve the efficiency and effectiveness of business operations. Customers nowadays demand quicker and more efficient service delivery, and automation in the supply chain has become crucial. Following are some of the business benefits of implementing automation in the supply chain:
Manual Workload Automation:
Today’s supply chains are not fully digitally optimized. Major processes usually depend on creating and passing spreadsheets, PDFs, and emails. Even ERP systems are not flexible enough to support digital business initiatives. This means that employees have to do a lot of manual work that could be automated to allow them to focus on other productive tasks. Supply chain automation eliminates manual tasks, reduces operational costs, and helps businesses reach operational excellence.
Improved Accuracy and Error Reduction:
It reduces the chances of human errors in inventory management and order fulfilment. Technologies like RFID and barcode scanning systems ensure accurate product tracking, leading to error reduction in inventory counts and order fulfilment.
Operations Transparency and Visibility:
Traditional supply chain processes lack transparency in inventory management and often cause unpredictable lead times. As more applications and systems are introduced to improve efficiency, the process often creates silos and gaps between them. A low-code automation platform can connect all apps and systems to create a centralized location for employees. They can easily access information, gain real-time data insights, get up-to-date status updates, and transfer information faster. This type of transparency would benefit customers and employees as they get an overview of how orders progress throughout the supply chain.
Enhanced Data Analytics and Decision-making:
Automation offers large amounts of data for businesses to analyze and gain insights into customer preferences, operational efficiency, and market trends. With an enhanced data-driven approach, businesses can make informed decisions and create strategic planning.
Improved Risk Management and Compliance:
An automated supply chain offers visibility across the entire process, enabling better risk management. It helps in identifying potential issues faster and provides solutions to mitigate risks. Also, automation ensures compliance with regulatory standards by providing traceable and accurate records crucial for fulfilling industry standards and legal requirements.
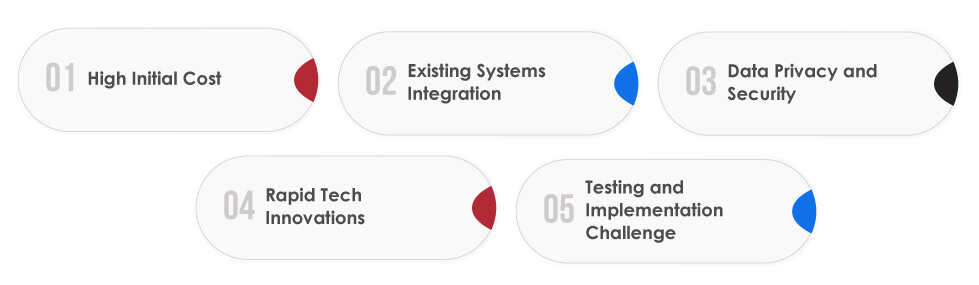
Challenges & Solutions of Supply Chain Automation
Although supply chain automation brings several benefits, it also presents challenges that need proper mitigation measures. Following are some of the challenges associated with supply chain automation:
High Initial Cost:
Intelligent automation technologies demand substantial upfront investment, which could challenge small and medium-sized enterprises. The cost includes technology implementation, infrastructure changes, etc. To counter this challenge, businesses can explore as-a-service models to lease a technology rather than buy it. It would be a cost-effective solution. The second option is to use phased implementation, starting with critical supply chain areas and distributing costs over time to make investment more manageable.
Existing Systems Integration:
Automation technologies require integration with legacy systems, which is technically and logistically challenging. This requires restructuring existing business processes and workflows and technical expertise. Using middleware solutions can lead to smoother integration, allowing new technologies to sync with older systems. Implementing phased integration strategies can enable businesses to test and adapt processes.
Data Privacy and Security:
Automated systems rely heavily on data, which raises serious concerns about data privacy and security issues such as data breaches, cyberattacks, and unauthorized access. Regular security audits, employee training, and compliance with data protection standards can help mitigate these issues. Encrypting sensitive data and using secure cloud-based solutions could also prove beneficial.
Rapid Tech Innovations:
Automation technology updates much faster, requiring businesses to constantly adapt and update their systems. This requires ongoing investment and training employees regarding new technologies. Establishing a dedicated department that keeps up to date with the latest tech innovations could be beneficial. It will ensure that the workforce uses and supports new technologies effectively.
Testing and Implementation Challenge:
Testing automated systems before full-scale implementation is challenging as it requires replicating real-world scenarios and ensuring systems sync seamlessly with existing processes. Partnering with a professional QA services provider and deploying test automation programs can help effectively test and implement supply chain automation.
Use Cases of Automation in Supply Chain
Integrating automation in the supply chain transforms how businesses manage logistics, operational efficiency, and inventory. The logistics automation market will reach $158 billion by 2032, reflecting its widespread adoption and success in supply chain management. Let’s take a close look at some of the use cases of automation in the supply chain:
Order Management using RPA:
Order management is a crucial part of the supply chain, consisting of many complexities like tracking, capturing, fulfilling, and managing customer orders. It contains many repetitive steps that need automation. RPA can handle this task. It saves time by automating order verification steps, pulling data from multiple sources, and eliminating duplicate orders without human input. For instance, smart bots work 24/7 to manage orders effectively despite no human involvement.
Invoice and Payment Management:
Businesses relying on manual invoice processing often face errors, payment delays, and discrepancies. With supply chain automation, businesses can improve their productivity by boosting accuracy and reducing the time employees spend processing invoices. For instance, invoice bots can download, scan/read invoices using OCR, capture email data, validate invoices, analyze payment deadlines, and automate invoice acceptance.
Supply Chain Analytics:
Big data analytics and AI in supply chain automation provide insights that are helpful in demand forecasting, identifying market trends, and aiding decision-making. Predictive analytics helps analyze potential disruptions, enabling businesses to manage risks and adjust their strategies accordingly.
Quality Control:
Quality control is one of the basic aspects of supply chain management. Using automation technologies like AI and RPA for quality control ensures that product standards are consistently met. Automated inspection systems using sensors and cameras detect defects faster and more accurately than human inspection, improving product quality.
Summary
In the digital business world, supply chain automation is necessary to upscale traditional supply chain operations. Using technologies like AI, RPA, and ML, businesses can transform processes such as inventory management, order processing, invoice processing, and payment management. Automation is an effective solution for seamless workflows, real-time reporting, and improving app integration. However, businesses need a robust test automation solution to ensure a seamless transition to supply chain automation.
How can Tx help with Supply Chain Automation?

Tx is a leading test automation services provider that can support you in the supply chain automation transition process. We facilitate automation strategically throughout the supply chain to identify the best approach based on the process characteristics and define the governance framework for engagement. Partnering with Tx offers you the following benefits:
• Validate supply chain and inventory management systems to ensure accurate tracking, real-time updates, and efficient order processing.
• Ensure compliance with industry standards, regulations, and data privacy laws such as GDPR, PCI DSS, HIPAA, and ADA to avoid penalties and maintain customer trust.
• E2E management of test automation lifecycle to ensure efficient execution and integration to enhance product quality and speed to market.
• Tailored advisory services to maximize efficiency, minimize risks, and ensure ROI in your supply chain automation process.
• Our test automation framework empowers you to accommodate the unique needs of supply chain systems, including integration with third-party apps and user devices.
• Our in-house accelerators, Tx-Automate, Tx-HyperAutomate, etc., can aid you in your transition to supply chain automation.
To know more, contact our QA experts now.
Discover more
Get in Touch
Stay Updated
Subscribe for more info