- Assessing the Threat Landscape of the Digital Workforce
- Building a Strong Security Infrastructure
- Establishing Robust Security Policies
- Securing Digital Infrastructure
- Importance of Security Testing in Digital Environment
- Accessibility Testing Tools for the Public Sector
- Conclusion
- Why Choose TestingXperts for Security Testing Services
Digital security has become a critical concern for organisations across industries. The threat landscape continuously evolves, with cybercriminals becoming more sophisticated and targeting the digital workforce. A recent Deloitte Center for Controllership poll found that many executives experienced cyber threats targeting their organisations’ accounting and financial data. Of those polled, 34.5% reported that cyber adversaries had targeted their data within the past year. Among this group, 22% experienced at least one cyber event, while 12.5% encountered multiple incidents.
Even more concerning is that almost half of the C-suite and other executives surveyed (48.8%) anticipate an increase in the number and scale of cyber events targeting their organisations’ accounting and financial data in the coming year. Surprisingly, only a mere 20.3% of respondents stated that their accounting and finance teams consistently collaborate closely with their counterparts in cybersecurity.
These findings highlight a significant gap between recognising cyber threats and integrating cybersecurity efforts within the digital workforce. Understanding the digital workforce is crucial to creating a secure environment. This workforce comprises remote employees, hybrid employees, contractors and freelancers who are heavily reliant on digital technologies. By gaining insights into their characteristics and dynamics, organisations can tailor security strategies to address specific vulnerabilities and risks.
Assessing the Threat Landscape of the Digital Workforce

Organisations must proactively assess the threat landscape to protect their digital workforce and valuable assets. By doing so, businesses can understand their threats and take appropriate actions to mitigate them.
The first step in assessing the threat landscape is identifying potential cybersecurity risks that threaten the digital workforce. This includes external risks such as sophisticated cyber-attacks, data breaches, malware infections, and internal risks like insider threats and human error. By recognising these risks, organisations can implement targeted security measures to minimise vulnerabilities and protect against potential attacks.
Common Security Challenges for Businesses
Businesses face numerous security challenges in today’s interconnected world. Following are some key challenges faced by the digital workspace in today’s technological world:
• The rapid adoption of cloud technologies and the Internet of Things (IoT) introduces new vulnerabilities like data breaches, unauthorised access, misconfiguration, data leakage, and supply chain attacks
• The increasing sophistication of cybercriminals poses constant threats
• Ensuring secure remote access for employees
• Protecting against social engineering attacks
• Managing the security implications of third-party vendors
The Impact of Inadequate Security Measures
Organisations must recognise the significance of investing in robust security measures and prioritising the protection of their digital workforce. Inadequate security measures can have severe consequences for organisations, such as:
• Financial losses resulting from data breaches and compliance penalties
Reputational damage and loss of customer trust
• Potential legal implications like intellectual property (IP) theft, data protection lawsuits, and regulatory compliance violations
• Disruption of business operations and low productivity
• Creation of a hostile work environment
Building a Strong Security Infrastructure
Organisations must establish a robust security infrastructure to develop a secure environment for the digital workforce. Companies should follow the following pointers to empower their workforce to safeguard their digital assets actively:
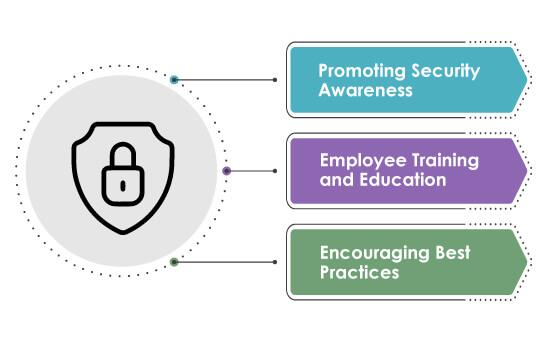
Promoting Security Awareness
It is a crucial step in building a strong security culture. Organisations can foster a sense of responsibility towards maintaining a secure environment by making employees aware of potential risks and threats. This includes educating employees about common cybersecurity threats, such as phishing attacks, social engineering, and malware, and providing practical tips for identifying and reporting potential security incidents. Regular communication channels, such as email updates, newsletters, and internal security bulletins, can disseminate important security information and reinforce the significance of security awareness.
Employee Training and Education
This step is vital in equipping the workforce with the necessary knowledge and skills to navigate the digital landscape securely. Training sessions should cover essential topics, including password hygiene, secure remote working practices, data protection, and incident response protocols. These training programs can be conducted through online modules, workshops, or interactive sessions encouraging employee participation. By investing in continuous education, organisations can ensure that employees stay up to date with the latest security practices and are well-equipped to mitigate potential risks.
Encouraging Best Practices
Encouraging best practices is an effective way to embed security into everyday workflows and behaviours. This includes establishing clear security policies and guidelines that define acceptable use of technology resources, password complexity requirements, and data handling procedures. Regular reminders and reinforcement of these best practices through internal communications, posters, and digital signage can help keep security top-of-mind for employees. Organisations should also consider implementing incentive programs or recognition initiatives to reward employees demonstrating exemplary security practices, fostering a positive security culture and encouraging widespread adoption of secure behaviours.
Establishing Robust Security Policies
By setting clear guidelines and implementing effective security policies, organisations can ensure that their digital workforce operates in a secure and protected environment.

Developing a Comprehensive Security Policy
This policy document should outline the organisation’s approach to security and guide it on protecting sensitive information, managing access rights, and addressing security incidents. It should also cover acceptable use policies for technology resources, guidelines for secure remote work, and data handling and disposal rules. Organisations can develop a well-rounded approach that aligns with industry best practices and regulatory requirements by involving key stakeholders, such as IT, legal, and HR departments.
Defining Access Control Measures
Organisations should define access levels and permissions based on job roles and responsibilities, implementing the principle of least privilege. This means granting employees access only to the resources necessary for their job functions. Organisations should regularly review and update access control lists to remove unnecessary requests. Implementing multi-factor authentication (MFA) is also recommended to add an extra layer of security and prevent unauthorised access. Organisations can significantly reduce the risk of unauthorised access and potential data breaches by defining and enforcing access control measures.
Implementing Strong Authentication Mechanisms
Robust authentication mechanisms are essential to verify the identity of users accessing digital resources. Passwords alone are no longer sufficient to protect against sophisticated attacks. Organisations should implement robust authentication methods such as biometrics, hardware tokens, or one-time passwords (OTP) in combination with passwords. Additionally, password management tools and regular password updates should be encouraged. By implementing robust authentication mechanisms, organisations can enhance the security of their digital workforce and protect against unauthorised access attempts.
Securing Digital Infrastructure
Organisations should establish a robust and resilient digital infrastructure that safeguards sensitive information and supports a secure digital workforce. Let us look into the following points that businesses should address when securing digital infrastructure:
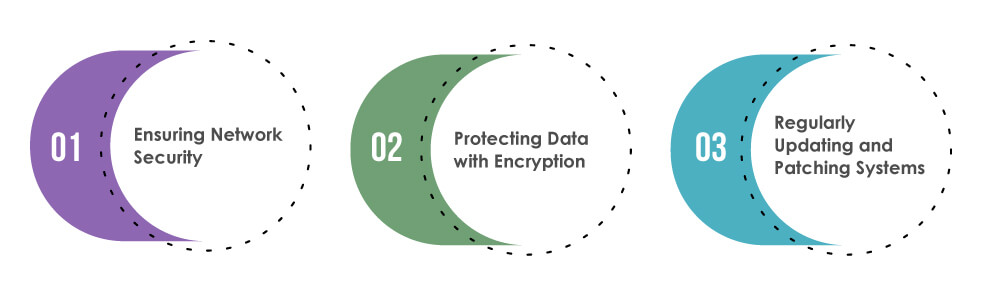
Ensuring Network Security
Organisations should implement security layers, including firewalls, intrusion detection and prevention systems, and network segmentation. Regular network monitoring and analysis help detect and mitigate potential threats promptly. Additionally, establishing secure remote access solutions, such as virtual private networks (VPNs), enhances the security of remote workers and reduces the risk of unauthorised access.
Protecting Data with Encryption
Data encryption plays a vital role in protecting sensitive information from unauthorised access. Organisations should implement robust encryption methods, such as Advanced Encryption Standard (AES), to safeguard data at rest and in transit. Encryption should be applied to sensitive files, databases, and communication channels. Organisations can add an extra layer of protection by employing encryption techniques, even if data is compromised or intercepted.
Regularly Updating and Patching Systems
Organisations should establish a systematic approach to patch management, ensuring that operating systems, applications, and firmware are updated with the latest security patches. Automated patching tools and processes can streamline this task and minimise the window of exposure to potential exploits. Regular vulnerability assessments and penetration testing can further identify weaknesses and guide the prioritisation of patching efforts.
Importance of Security Testing in Digital Environment
Security testing is crucial in today’s threat landscape, where cyber-attacks are becoming increasingly sophisticated and prevalent. It helps organisations identify vulnerabilities and weaknesses in the systems, applications, and networks before cybercriminals can exploit them. Organisations can uncover potential entry points and implement security protocols to protect against unauthorised access, data breaches, and other security incidents by conducting security testing.
Types of Security Testing
Various kinds of security testing can be employed to assess and strengthen the security of digital infrastructures:
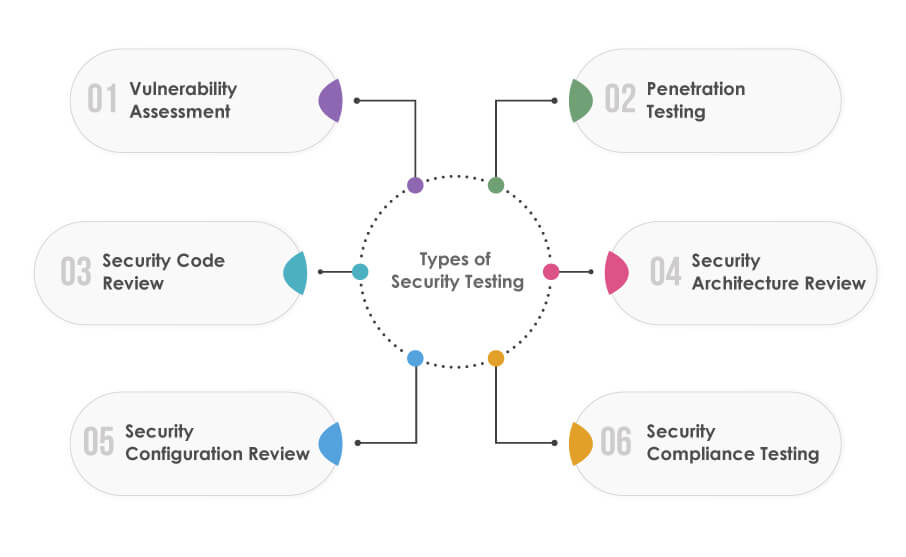
Vulnerability Assessment
Identifying vulnerabilities and weaknesses in systems, networks, and applications.
Penetration Testing
Simulating real-world attacks to evaluate the effectiveness of existing security controls and identify areas for improvement.
Security Code Review
Analysing the codebase for security flaws and vulnerabilities that could be exploited.
Security Architecture Review
Evaluating the overall security architecture to identify design flaws and potential vulnerabilities.
Security Configuration Review
Assessing the configuration settings of systems and applications to ensure compliance with security best practices.
Security Compliance Testing
Verifying adherence to industry regulations and standards, such as GDPR or ISO 27001.
Incorporating Security Testing in the Development Lifecycle
By incorporating security testing from the early stages of development, organisations can identify and rectify security issues at the root, avoiding costly fixes and mitigating potential risks. This includes conducting security code reviews, performing vulnerability assessments, and engaging in penetration testing throughout development. Additionally, organisations should establish a culture of continuous testing and security awareness, promoting collaboration between development teams and security experts.
Conclusion
With cyber threats on the rise and sensitive data at risk, organisations must adopt comprehensive security measures to protect their digital assets. By building a strong security culture, establishing robust security policies, and securing the digital infrastructure, businesses can fortify their defences, safeguard valuable information, and foster a culture of security within their workforce. Organisations can build employee, stakeholder, and customer confidence by prioritising a secure digital workforce environment. With proper security testing measures, businesses can protect sensitive data, maintain regulatory compliance, and mitigate the financial and reputational risks associated with data breaches.
Why Choose TestingXperts for Security Testing?

TestingXperts offers a unique combination of expertise, comprehensive services, and a proven track record for securing and validating your digital workforce’s integrity. From their knowledge and experience to their wide range of security testing services, TestingXperts offers various benefits to its clients:
• A dedicated team of skilled professionals specialising in both security testing
• Extensive experience in assessing and fortifying the security and integrity of digital infrastructures
• In-depth knowledge of industry best practices, regulatory requirements, and emerging technologies
• The ability to tailor testing approaches to the specific needs of organisations and their digital workforce
• A comprehensive suite of security testing services covering various aspects of your digital infrastructure
• Services include vulnerability assessments, penetration testing, code reviews, data integrity testing, data validation, and more
• Customised solutions to address unique security testing requirements, ensuring a thorough evaluation and validation process
Contact TestingXperts today to learn more about our comprehensive security testing services and secure your digital workforce.
Discover more
Get in Touch
Stay Updated
Subscribe for more info