
Table of Contents
- Why is Payment Security Necessary for eCommerce Business?
- Understanding PCI DSS Requirements
- Risks of Non-Compliance
- Steps to Ensure Compliance for eCommerce Stores
- PCI DSS Compliance Testing
- Conclusion
- How Can TestingXperts Help with Compliance Testing for eCommerce Stores?
With the exponential growth of online shopping in recent years, ensuring payment security on eCommerce stores and platforms has become crucial. As the eCommerce industry grows, so does the importance of adhering to standards that protect businesses and their customers. PCI DSS is one of the core frameworks to ensure payment card safety in the digital world. But what exactly is it, and why should online retailers care?
PCI DSS stands for Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard. Established by major credit card companies like Visa, MasterCard, and American Express, it is a set of requirements designed to ensure that any company that processes, stores, or transmits credit card information does so in a secure environment.
For businesses, being PCI DSS compliant is not just a recommendation; it is often a requirement. Not only does it help protect sensitive customer data, but it also shields businesses from potential financial penalties and legal consequences resulting from data breaches.
In an age where a single breach can devastate a company’s reputation, the importance of PCI DSS cannot be overstated. Knowing a retailer is PCI DSS compliant gives consumers the confidence to shop with peace of mind, knowing their payment information is safe.
Why is Payment Security Necessary for eCommerce Business?
eCommerce businesses deal with abundant sensitive information. Cybercriminals are eager to exploit sensitive data, from home addresses to payment details. Ensuring payment security is not about securing credit card details but creating an overall environment where customers feel their data is respected and protected.
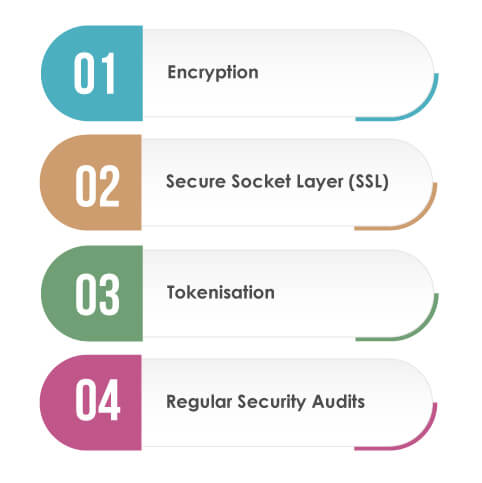
Several layers contribute to this security:
Encryption
Encrypting data ensures that the information remains unintelligible to unauthorised parties even if intercepted.
Secure Socket Layer (SSL)
SSL certificates ensure secure data transfer, especially during transactions. Most shoppers now look for the padlock symbol in their browsers before purchasing.
Tokenisation
Instead of storing sensitive card details, systems can use tokens representing the card data without exposing the actual information.
Regular Security Audits
Ensuring an eCommerce platform is checked for vulnerabilities and keeping software up to date are pivotal to maintaining a secure environment.
Understanding PCI DSS Requirements
The PCI DSS is built around 12 fundamental requirements, broken into six broader categories. These requirements serve as a roadmap for businesses to safeguard customer payment data:

Build and Maintain a Secure Network and Systems
• Install and maintain a firewall configuration to protect cardholder data
• Change vendor-supplied defaults for system passwords and other security parameters
Protect Cardholder Data
• Protect stored cardholder data
• Encrypt transmission of cardholder data across open, public networks
Maintain a Vulnerability Management Programme
• Use and regularly update anti-virus software or programs
• Develop and maintain secure systems and applications
Implement Strong Access Control Measures
• Assign a unique ID to each person with computer access
•Restrict physical access to cardholder data
Regularly Monitor and Test Networks
• Track and monitor all access to network resources and cardholder data
• Regularly test security systems and processes
Maintain an Information Security Policy
• Maintain a policy that addresses information security for all personnel
It is essential to familiarise oneself with some key definitions to understand PCI DSS:
Cardholder Data (CHD)
This refers to any information printed, processed, transmitted, or stored in any form on a payment card. It encompasses the cardholder’s primary account number (PAN), cardholder name, expiry date, and service code.
Sensitive Authentication Data (SAD)
It is related to the information used to authenticate cardholders and confirm payment card transactions. It includes full magnetic stripe data, CAV2/CVC2/CVV2/CID, and PINs/PIN blocks. It is important to note that SAD should never be stored post-authorization.
Merchant
Any business entity that accepts payment cards bearing the logos of any of the five members of the Payment Card Industry Security Standards Council (PCI SSC) – American Express, Discover, JCB, MasterCard, and Visa – as payment for goods or services.
Service Provider
A business entity, excluding the payment brands, directly involved in processing, storing, or transmitting cardholder data on behalf of another entity.
Risks of Non-Compliance
Safeguarding customer payment data is not just a matter of ethical business practice. It also helps avoid substantial financial and reputational risks. Many eCommerce businesses underestimate the implications of non-compliance with PCI DSS, but doing so can lead to severe consequences.
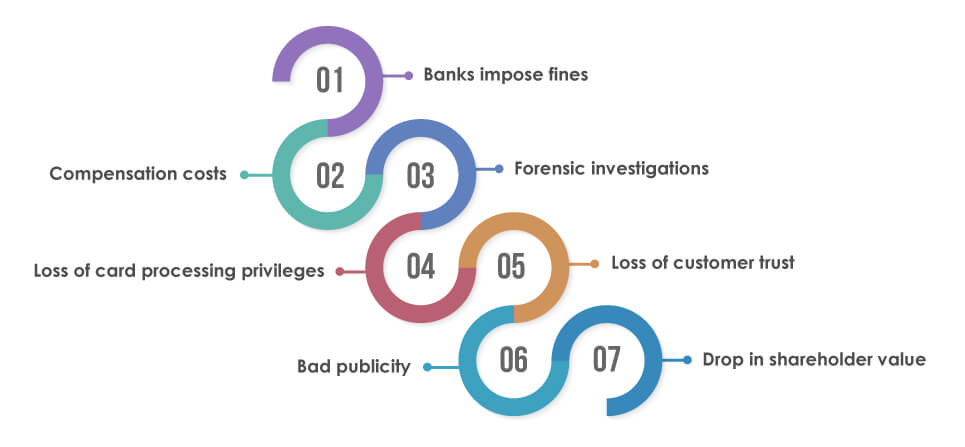
Not being able to comply with PCI DSS compliance exposes businesses to potential fines and penalties:
Banks impose fines
The banks that process payment card transactions can fine for non-compliance. These fines range from a few thousand pounds and can escalate to tens or even hundreds of thousands of pounds for repeated violations or in case of a data breach.
Compensation costs
If a business suffers a data breach due to non-compliance, it must compensate affected customers. These compensations cover fraudulent transactions and credit monitoring services.
Forensic investigations
Post a breach, the business might need to conduct a forensic examination to determine the cause and extent of the breach. Such investigations come at a substantial cost.
Loss of card processing privileges
In extreme cases of non-compliance, the license to process card transactions can be revoked. For an eCommerce business, this spells disaster, significantly hampering sales and operations.
Loss of customer trust
Customers entrust their payment data to eCommerce businesses, expecting it to be kept safe. A breach shatters this trust, making it challenging to rebuild. Many customers might choose never to shop at that eCommerce store again.
Bad publicity
Data breaches, especially payment information-related, attract media attention. Negative press can tarnish a brand image, leading to declining sales and profitability.
Drop in shareholder value
For a publicly traded company, news of non-compliance or a related data breach can negatively impact their stock price, affecting shareholder value.
Steps to Ensure Compliance for eCommerce Stores
Achieving and maintaining PCI DSS compliance requires proactive action. Let us explore the crucial steps eCommerce stores should take:
Securing Cardholder Data: Storage, Transmission, and Encryption
Securing cardholder data remains the key aspect of PCI DSS compliance. Here is how to ensure that cardholder data is secure:
Limit data storage
Only store cardholder data if essential. Regularly audit and delete unnecessary stored data.
Use robust encryption
When transmitting cardholder data across open, public networks, use strong cryptography and security protocols, such as SSL/TLS or IPSEC, to safeguard sensitive cardholder data during transmission.
Protect stored data
Implement encryption, truncation, tokenisation, or masking to protect stored cardholder data. Avoid storing sensitive authentication data after transaction authorisation.
Regularly Testing and Monitoring Security Systems
There needs to be more than a static approach to security. Continuous monitoring is the key:
Conduct vulnerability scans
Regularly scan the systems for vulnerabilities. Many third-party providers offer services that identify potential weak points in your network.
Perform penetration tests
Periodically test to see how well systems can fend off attacks. These tests simulate cyberattacks, helping identify areas of improvement.
Monitor access logs
Keep a keen eye on who accesses the systems. Suspicious activity can hint at potential security threats.
Implementing Strong Access Control Measures
Only some people within the business need access to cardholder data. It is important to restrict and monitor access:
Role-based access
Assign access to cardholder data based on job roles. Only provide access to employees who need it for their job functions.
Use unique IDs
Ensure each person with computer access has a unique ID. It helps in tracking and monitoring individual access.
Two-factor authentication
Implement two-factor authentication for added security, especially for remote access. It requires users to provide two separate forms of identification before gaining access.
Regularly Testing and Monitoring Security Systems
There needs to be more than a static approach to security. Continuous monitoring is the key:
Conduct vulnerability scans
Regularly scan the systems for vulnerabilities. Many third-party providers offer services that identify potential weak points in your network.
Perform penetration tests
Periodically test to see how well systems can fend off attacks. These tests simulate cyberattacks, helping identify areas of improvement.
Monitor access logs
Keep a keen eye on who accesses the systems. Suspicious activity can hint at potential security threats.
Implementing Strong Access Control Measures
Only some people within the business need access to cardholder data. It is important to restrict and monitor access:
Role-based access
Assign access to cardholder data based on job roles. Only provide access to employees who need it for their job functions.
Use unique IDs
Ensure each person with computer access has a unique ID. It helps in tracking and monitoring individual access.
Two-factor authentication
Implement two-factor authentication for added security, especially for remote access. It requires users to provide two separate forms of identification before gaining access.
Maintaining an Information Security Policy
Lastly, but most importantly, instil a culture of security:
Document policies
Have a clear, written policy detailing all security measures. Ensure all employees understand and commit to following this policy.
Ongoing training
Regularly train staff on the importance of cardholder data security and the practices they should follow.
Review and update
The digital landscape evolves, and so do threats. Regularly review and update information security policy to stay ahead of potential risks.
PCI DSS Compliance Testing
Compliance testing evaluates the security measures of an eCommerce platform against the PCI DSS standards. It identifies areas of non-compliance, highlighting vulnerabilities that cybercriminals could exploit.
Consistent testing ensures that your systems remain resilient against evolving cyber threats. It guarantees that any changes or updates to your eCommerce platform do not introduce new vulnerabilities. Furthermore, regular testing helps businesses stay aligned with the evolving PCI DSS standards.
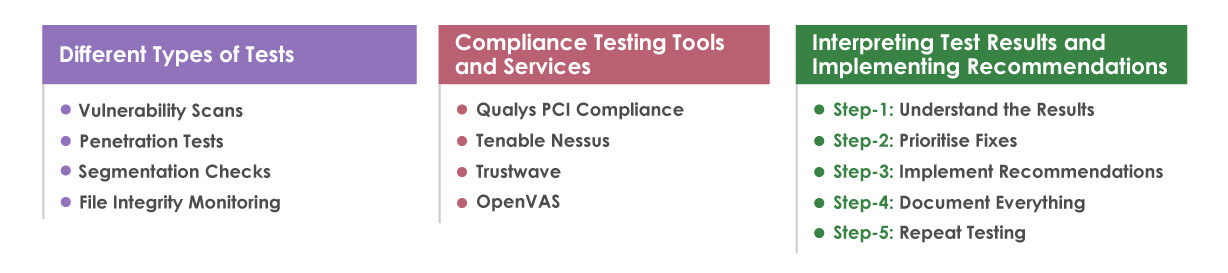
Different Types of Tests
Vulnerability Scans
These automated, non-intrusive scans check a system for known vulnerabilities. They are a good starting point but need to be complemented by more in-depth tests.
Penetration Tests
These involve simulating cyber-attacks on a system to identify vulnerabilities not detected in vulnerability scans. It gives a real-world perspective on potential security threats.
Segmentation Checks
These determine if the segmentation methods effectively isolate cardholder data from other networks.
File Integrity Monitoring
This checks for unauthorised changes to critical system files, configurations, and content files, providing alerts if any discrepancies are detected.
Compliance Testing Tools and Services
Various tools and services facilitate effective PCI DSS compliance testing:
Qualys PCI Compliance
It is an automated tool that finds and seals security gaps. It offers comprehensive vulnerability scanning and helps in generating necessary compliance reports.
Tenable Nessus
It is a widely known vulnerability scanning tool that identifies vulnerabilities, configuration issues, and more.
Trustwave
This tool provides testing services, including vulnerability scans, penetration testing, and risk assessments.
OpenVAS
A free, open-source vulnerability scanning tool that can identify potential weak points in your system.
Interpreting Test Results and Implementing Recommendations
Step-1: Understand the Results
Work with cybersecurity professionals to understand the test results thoroughly. Not all vulnerabilities carry the same priority. Determine which ones require immediate attention.
Step-2: Prioritise Fixes
Address the most critical vulnerabilities, especially those that pose immediate threats to cardholder data.
Step-3: Implement Recommendations
Use the test insights to implement security enhancements. It involves software updates, configuration changes, or even overhauls of specific processes.
Step-4: Document Everything
For compliance purposes and future reference, document all test results, the steps taken to address vulnerabilities, and any changes made to the system.
Step-5: Repeat Testing
After implementing changes, re-test to ensure the vulnerabilities have been effectively addressed. Regularly schedule compliance tests to maintain a robust security posture.
Conclusion
eCommerce presents businesses with unparalleled opportunities for growth and customer engagement. However, as online transactions multiply, so do the responsibilities of ensuring secure exchanges of sensitive information. The significance of PCI DSS compliance is a cornerstone of effective and trustworthy online business operations. From understanding the core requirements to the rigorous compliance testing processes, maintaining a secure environment is an ongoing commitment. As cyber threats evolve and diversify, periodic evaluations and enhancements of security protocols are not optional but a business imperative. Businesses that diligently uphold these standards safeguard their operations and fortify their standing in a competitive digital marketplace.
How Can TestingXperts Help with Compliance Testing for eCommerce Stores?
TestingXperts offers tailored compliance testing services, ensuring your online store stands robust against evolving cyber threats and regulatory mandates. We combine expertise, innovation, and experience to deliver unparalleled results for your eCommerce platform. Here is what sets us apart:

Expertise in PCI DSS Standards
Our team comprises QA professionals with a deep knowledge of the PCI DSS standards. We understand the intricacies of the eCommerce sector and tailor our strategies to align with your specific needs.
Comprehensive Testing Suite
From vulnerability scans and penetration testing to segmentation checks and file integrity monitoring, we offer a wide range of testing services, ensuring no vulnerability goes unnoticed.
Innovative Tools and Technologies
We leverage the latest tools in the industry, combined with custom solutions, to provide precise, effective, and timely results.
Continuous Monitoring
We offer continuous monitoring services, ensuring your platform remains compliant and secure amidst the ever-evolving cyber threats.
Transparent Reporting
Our detailed reports provide actionable insights, helping you understand vulnerabilities and implement effective countermeasures.
Tailored Solutions
Every eCommerce store is unique. We offer bespoke testing strategies tailored to your platform’s architecture, needs, and challenges.
Contact our QA experts now to find out more about TestingXpert’s compliance testing services.
Discover more
Get in Touch
Stay Updated
Subscribe for more info




