Most businesses today depend on mobile applications for enabling their businesses and these applications form the most dominant way of delivering services to their customers. Many enterprises have been investing heavily in getting business apps to enchant their digital customers. But, these apps should upkeep specific benchmarks such as effective user experience, flawless performance, and quick loading. Both mobile and web applications should deliver excellent customer experience and should not have any glitches to ensure its success.
Why Mobile App Testing
Further, to retain mobile app customers, it is vital for these apps to be stable and perform flawlessly as per user expectations. Hence, as part of achieving efficient applications, mobile application testing plays a critical role in their success. It is a process used to test the functionality, usability, performance, consistency and other factors of the software developed for handheld devices. But, the process of mobile app testing has its challenges. Hence, it becomes a daunting task for testing mobile apps with varied factors to be considered; operating systems (OS), device types, diverse usage scenarios, and network compatibility.
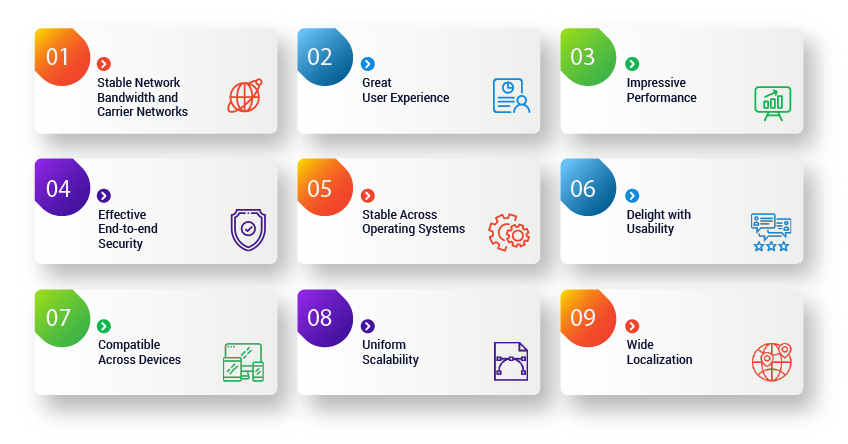
What Factors to Consider for Mobile Application Testing?
1. Stable Network Bandwidth and Carrier Networks:
There is a dense impact of internet bandwidth on mobile apps. A typically slow or a bad internet connection adversely affects the mobile application behavior for different users. Mostly, users don’t wait for longer than 3 seconds for an app page to load. Hence, mobile testing should be taken up to check the impact of interruptions and network fluctuations.
Specifically, Interruption testing is a process to replicate abrupt or unexpected interruptions in the app such as battery removal, OS upgrade, plug in and out of charging, network loss and restoration, and device shut down, to name a few. Thus, it is essential to test mobile apps in actual network environments to get a real picture of mobile application behavior.
Mobile apps are usually developed to support multiple geographical locations and are available in multiple languages to engage end-users. These apps should be tested across carrier networks geo-location wise to ensure the app’s correct usage in different locations.
2. Great User Experience (CX):
The most important impression of any mobile app is the necessity to deliver a smooth and winning user interface. The user interface should be simple, effective and easy to navigate for the users. Hence, the mobile app should be tested with the mobile testing method of user-interface crowd testing. This helps to understand the initial response and feedback from real-time users. It also helps to test the app in real-world conditions with users from different locations to get a first-hand look and feel about the app.
3. Impressive Performance:
Mobile app users expect a good response from the application while using it. The app performance is measured by how responsive it is, how quickly it starts up, how well it uses its device memory, and how efficiently it uses its device power, etc. Moreover, a user’s expectation of responsiveness alters with the mobile device they are using. Optimizing screen size is an important aspect to deliver excellent app performance. Performance testing should necessarily be taken up to ensure flawless app performance as malfunctioning might lead to disengaged users
4. Effective End-to-End Security:
With the cyber-threats all around and especially mobile apps being largely attacked, it is essential to get them thoroughly tested for security. Users demand their personal data safety, and secure transactions. For the mobile apps to perform stable payment integrations, end-to-end security testing should be taken up. Security testing helps to identify threats and vulnerabilities if any in the app and ensures data security.
5. Stable Across Operating Systems:
There are various mobile operating systems (iOS, Android, Windows 10, etc.) in usage, and each of these operating systems has multiple versions. There is a complexity of the supported platforms that have indeed gone to a new level. Typically, businesses should make sure that their mobile applications should perform well on all operating systems and their supported versions. To achieve compatibility across OS, effective end-to-end mobile app testing should be taken up across OS versions.
6. Delight with Usability:
Mobile apps should be user-friendly and intuitive to attract baby boomers, novice users as well as experienced users. The app should be interactive with a good look and feel and ensure effective navigation all through the functionalities. Complicated user flows confuse the users, and they might even restrain from using such mobile apps. Thus, usability testing should be taken to ensure the app has a smooth and straightforward flow all along with the functionalities.
7. Compatible Across Devices:
There are numerous types of mobile devices, and the mobile application should perform as expected across a combination of mobile devices and browsers. Mobile compatibility testing should be enforced to check the app compatibility on different devices and browser combinations to verify screens and behavior as expected. Compatibility testing is usually performed for the following:
– Testing across Databases such as Oracle, SQL Server, etc.
– Testing cross-wise over Web browsers such as IE, Chrome, Firefox, Mozilla, Safari, etc.
– Testing across System Software such as web server and updates
– Testing Cross-wise across various mobile platforms, devices, networks
Hence, with the diversity of devices, platforms, screen resolutions, memory sizes, and connectivity options, mobile compatibility testing helps to ensure the mobile app is compatible across all these variations.
8. Uniform Scalability:
When once the mobile app becomes popular, there is an evident increase in the number of users, and sometimes the growth could be exponential. Hence, it becomes apparent to test the mobile app for its scalability with increased and decreased user loads using Load testing. Load testing helps to decipher whether the app can scale when numerous users access it at the same time.
9. Wide Localization:
It is also essential that a mobile app should adhere to the regional settings; customizing the app according to the target country/region with a linguistic touch for mobile app success. Hence, localization testing is necessary to ensure the app balances the cultural and linguistic aspects of a particular region. Linguistic testing, cultural testing, cosmetic testing, and functional testing should be taken up to ensure an all effective mobile app that truly enchants the end-users.
What are the tips to select best mobile app testing tool?
Cross-Platform Support:
The chosen mobile testing tool should be able to support devices across various platforms and operating supports.
Reusability:
The testing tool should provide the ability to reuse the testing scripts as this saves time and effort of the teams.
Support for Vendor:
The selected tool should support the vendor on all scenarios such as for installation, for maintenance, device availability on the tool, etc.
Cost:
When planning for a tool, the cost is one of the important factors to be considered, hence it should be analysed whether the ownership of the tool is under the budget of the enterprise or not.
Integration with other tools:
The mobile testing tool should have the ability to get integrated with other test management tools, application lifecycle management, and help in communicating with all stakeholders.
Cross-Browser Support:
Testing is essential across various browsers such as Chrome, Internet Explorer, Safari, Firefox, etc. to check the app performance. Therefore, it is important to consider a tool that provides cross-browser support.
What are the popular tools for mobile app testing?
Appium:
This is a cross-platform test automation tool for native and hybrid iOS. This open-source tool supports various programming languages such as Ruby, C#, Java, etc. Also, it supports Android versions above 2.3 and uses WebDriver interfaces to run test cases.
Robotium:
This is an open-source tool that is exclusively processed to test android applications. In this tool, the test cases are written in Java and it is widely known for writing automated black-box test cases. This tool helps a tester to perform various activities and benefits to write test cases in lesser time.
Test Project:
This is the world’s first community-powered test automation platform that helps users to perform tests over android, iOS, and web applications across operating systems. This free cloud-based tool can easily collaborate with the teams that are using Appium and Selenium to ensure speed and quality.
Testdroid:
This is a cloud-based mobile application testing tool that helps the teams to speed up the product delivery to the market, it helps the developers to save the app development costs, and reduces the unexpected scenarios of unpredictable costs. With the usage of this tool, it becomes the easiest and the fastest way to test the application over android and iOS devices across different screen resolutions, OS versions, and hardware platforms.
Calabash:
This is a mobile application testing framework working across multiple languages. Calabash has a list of libraries that help a test-code to technically interact with the hybrid and native apps.
Pitfalls to avoid with Mobile App testing
Mobile app testing plays an important role in app success but at the same time, there are few pitfalls that teams should take care of to ensure high-quality apps are released in the market.
Following are some of the pitfalls to avoid with mobile app testing:
1. Avoidance of UI/UX guidelines:
As a tester, it is necessary to comply with UI/UX guidelines for testing an Android or iOS app. These guidelines will help a tester to develop the front-end of a mobile app that is user-friendly, highly interactive and easy to navigate. Hence, mobile app testers must have properly drafted UI/UX guidelines that are in-line with the testing standards to ensure high-quality apps are released.
2. Incoherent use of testing methods:
Testing every aspect of a mobile app is not considered a good practice. It will in turn waste time and contribute to increased costs. It is better for a tester to first have an in-depth understanding of the app’s features and how it is going to create value for the users. Then a context-driven testing methodology can be prepared by the testers, which will guide them (testers) to test only on the specific aspects of the mobile app.
3. Too much emphasis on automation:
Automating too many aspects of a mobile app isn’t feasible. In fact, automating the features of a mobile app is more complicated when compared to automated software applications. Automating only those specific functionalities of a mobile app that really counts needs to be considered and taken care of. The mobile test pyramid is a strategic approach for performing automation on mobile applications.
4. Lack of strategic planning:
Implementing testing on mobile apps is a time-consuming and methodical process that needs to be carried out meticulously. Without a strategic plan, it leads to more ambiguity and complexity while testing mobile apps. Hence, testers should initially do the necessary groundwork to come up with a strategic plan of action that will make the mobile app testing process less cumbersome.
Conclusion:
It is critical and worth considering that today’s world has undoubtedly become mobile-first with an exponential increase in the usage of connected devices. Therefore, it is critical that all mobile apps should load quickly, have an excellent user interface, be scalable, deliver effective usability, flawless performance and thus ensure a great customer experience. In order to achieve all these factors, the end-to-end testing of mobile apps by independent mobile application testing companies should be leveraged. Such engagement with a Next-gen Specialist QA services provider ensures success to your mobile apps.
Related Queries on Mobile testing
Q1. What is meant by mobile testing?
Ans. Mobile Testing is a process used to test the functionality, usability, performance, consistency and other factors of the software developed for handheld devices.
Q2. How do you test mobile applications?
Ans. By using mobile app testing tools but the chosen mobile testing tool should be able to support devices across various platforms and operating supports.
Q3. What should I test in mobile application?
Ans. Through mobile application testing you can check functionality, performance, consistency, usability and user experience of the app.
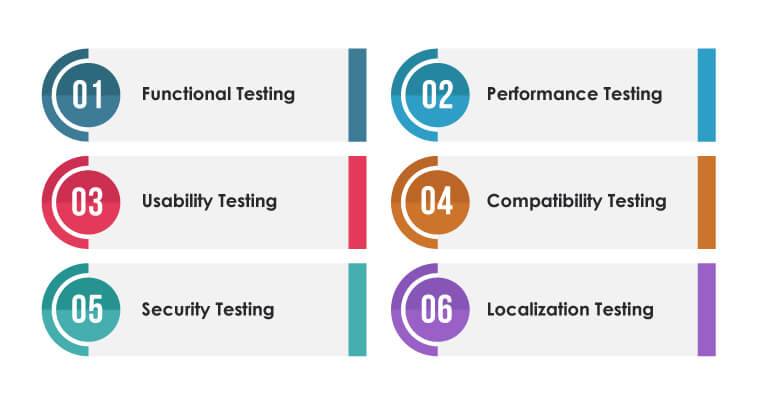
Q4. What are the types of mobile testing?
Ans. Types of mobile testing includes functional testing, usability testing, compatibility testing, Performance testing and security testing.
Discover more
Get in Touch
Stay Updated
Subscribe for more info