The global financial technology (FinTech) market is predicted to grow at a CAGR of 8.6% by 2024. This growth is driven by the significant rise of eCommerce and the increasing acceptance of digital payments and mobile banking. The high market growth makes the FinTech industry attractive for startups, investors, and cybercriminals. FinTech businesses manage sensitive financial information, but data storage, cross-platform malware infections, and other cyber vulnerabilities are always a concern that may impact critical data.
Content
- Some Infamous Cyber Attacks of the FinTech Industry in 2025
- Why is Fintech app security important?
- Key challenges of FinTech app security
- Common FinTech data protection regulations
- How to ensure FinTech apps security in 2025
- Top FinTech app security Testing Tools
- Conclusion
- How Can TestingXperts Help?
Some Infamous Cyber Attacks of the FinTech Industry in 2025

Unfortunately, cyberattacks and breaches make news frequently – hackers worldwide are always looking to tamper with unsecure data and breach immature security protocols. Here are some of the few FinTech cyber-attacks reported in 2022 so far.
• OP Financial Group, the biggest Finland bank, suffered a cyberattack in which phishing messages, claiming to be from a bank, asked recipients to click on a link to confirm the payment
• Threat actors exploited a critical vulnerability in the MOVEit file transfer software, compromising sensitive data from numerous organizations, including several financial institutions. The stolen data included personally identifiable information (PII), financial data, and proprietary business information.
• Orbit Chain, a blockchain platform, suffered a security breach resulting in a loss of $86 million in various cryptocurrencies, including Ether, Dai, Tether, and USD Coin. This attack involved multiple unauthorized transactions by unidentified hackers and was one of the notable fintech hacks of the year.
• On November 7, Finastra, a leading financial technology firm serving 45 of the top 50 banks, experienced a breach. The attacker accessed the system and stole 400 gigabytes of data. The breach was due to compromised credentials and did not affect other systems or operations.
• Qubit Finance was targeted by threat actors and compromised $80 million worth of cryptocurrency.
• Aon suffered a ransomware attack that caused limited disruption to several of its services.
• In May, Evolve Bank & Trust, which provides banking-as-a-service to fintech companies, was targeted by a ransomware attack. The personal information of over 7.6 million individuals was stolen, affecting clients like Affirm Holdings and Wise.
Why is Fintech app security important??

Cybersecurity in FinTech is key to protecting personal and financial data. Many businesses offer mobile banking, electronic payments systems, and crypto trading with security risks. As the FinTech sector expands, financial service providers are prime targets for criminals. If a FinTech app fails to protect customer data, it may lead to severe consequences such as:
• Financial losses to customers
• Identity theft
• Misuse of customer data to perform phishing and other cyber crimes
• Loss of trust as a brand
• Legal implications as per compliances such as GDPR and PCI DSS
• Increased risk of phishing and other subsequent attacks
According to Global FinTech Market 2021, the sector is estimated to grow at a CAGR of 26.87%, reaching $31.5bn by 2026. As the FinTech market grows and attracts more hackers and intruders, common challenges of FinTech apps have emerged that are proving to be a roadblock to secure innovation.
Key challenges of FinTech app security
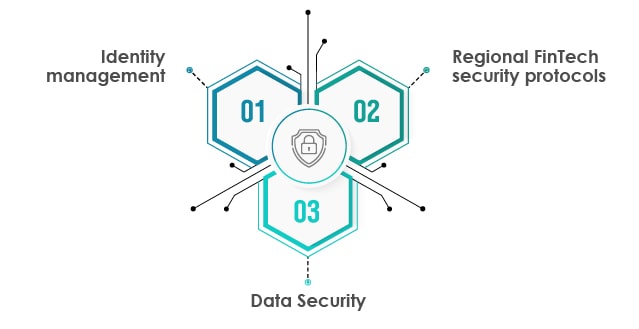
Identity management:
Seamless sharing of data is an essential attribute of FinTech. Since financial organizations gather loads of sensitive data, it creates concerns like data ownership and digital identity management. FinTech businesses must adhere to all necessary compliances to collect, manage, and store critical customer data to ensure maximum protection for customers’ data.
Data Security:
Hackers can exploit system weaknesses of FinTech apps and access critical data such as credit information, contacts, personal data, etc., and use it for financial fraud and data theft. Data security in FinTech should be of the top concern since it has been identified as the top concern for 70% of banks consulted during the Sixth Annual Bank Survey.
Regional FinTech security protocols:
FinTech applications should adhere to KYC (Know Your Customer) protocols as well as regional data protection regulations. For example, businesses that offer financial services in the European Union and the European Economic Area must abide by GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation). Non-adherence to these regulations can result in cyberattacks and huge fines from local governing bodies for non-compliance and exposing the data of users to non-reliable sources.
Common FinTech data protection regulations
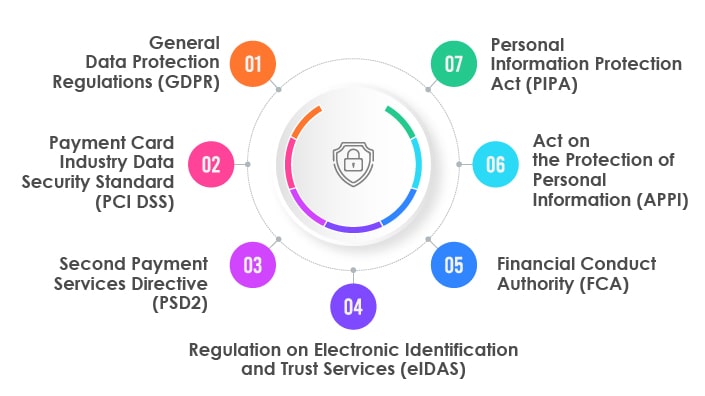
Based on the FinTech company’s location and target markets, specific data protection regulations and compliance must be adhered to in the financial services industry. Some of the critical data protection regulations are as under:
General Data Protection Regulations (GDPR):
GDPR is essential compliance for businesses that offer financial services in the European Union and the European Economic Area. FinTech apps should comply with GDPR to ensure secure data storage for EU residents.
Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS):
Data protection and compliance for businesses that manage credit card information. FinTech businesses should ensure their app is compliant with PCI DSS as it will optimize the security of credit, debit, and cash transactions and protect app users against any misuse of personal information.
Second Payment Services Directive (PSD2):
Regulation for electronic payments and cross-border transactions in Europe. FinTech apps compliant with PSD2 regulations can benefit from the security against cyber threats for processing electronic payments and safeguarding consumers’ financial data.
Regulation on Electronic Identification and Trust Services (eIDAS):
Provides a legal platform for transitions between FinTech organizations, businesses, government bodies, and citizens in the EU. eIDAS-compliant Fintech apps provide a consistent and legal framework for accepting electronic identities and signatures.
Financial Conduct Authority (FCA):
Data protection regulations for FinTech firms providing services in the United Kingdom. Since FCA is a renowned compliance body, FinTech app companies should consider FCA compliance to increase customer confidence and trust.
Act on the Protection of Personal Information (APPI):
Essential regulation for FinTech businesses managing data of Japanese residents. Apps compliant with APPI mean that the apps have enabled necessary cybersecurity measures that will secure the personal information of the app users.
Personal Information Protection Act (PIPA):
Essential regulation for FinTech businesses managing data of South Korean residents. PIPA compliance requires the data controllers and collectors to integrate technical, administrative, and physical measures for securing customers’ data against loss, theft, alteration, or damage.
Along with being compliant with the respective data protection regulations, FinTech applications should adhere to the latest best practices to ensure cybersecurity.
How to ensure FinTech apps security in 2025
Security must be the top priority for every FinTech company. They must safeguard their customers’ data. Here are the essential steps for making a secure FinTech app.
Implement multi-factor authentication:
Considering the sophistication and ability of cyber attackers, FinTech businesses cannot solely rely on passwords to protect their customers. When building a FinTech app, it is advised to implement multi-factor authentication where users prove their identity by making two or more claims.
Use code obfuscation:
Cybercriminals can clone a FinTech app in order to collect personal user data disguise. FinTech businesses should consider code obfuscation to prevent app cloning. Code obfuscation includes encrypting the code, removing revealing metadata, naming classes and variables with meaningless labels, or adding unused or meaningless code to an application binary.
Data encryption:
Encryption is the scrambling of data in order to hide critical information from unauthorized users. Cryptographic tools such as cryptographic hash functions may be leveraged to convert plaintext to ciphertext. Businesses should use encryption when releasing a FinTech app to protect critical customer data at rest or in transition.
Secure APIs:
Creating, testing, and integrating APIs is a part of building FinTech apps. Organizations design, develop, and consume APIs as part of building a FinTech app. Cyber-attackers often target APIs to breach the system and steal critical finance data. FinTech businesses can secure their app APIs by implementing the following methods:
• Implement the OAuth 2.0 standard
• Use authentication tokens
• Encrypt your data and use digital signatures
• Proactively identify and address API vulnerabilities
• Use quotas, throttling, and API gateways
AI and Machine Learning:
AI-driven security solutions can learn from past incidents to predict and prevent future security threats. They can detect abnormal behaviours and potential fraud in real-time.
Blockchain Technology:
With its decentralized nature and cryptographic security, blockchain can offer enhanced security for transactions and data storage.
Security Information and Event Management (SIEM):
SIEM systems provide real-time analysis of security alerts and help organizations to track and respond to incidents.
Cloud Security Tools:
With many FinTech apps leveraging cloud technologies, cloud security tools help protect data stored off-premises and ensure secure data transmission.
Perform Penetration Testing
Penetration testing refers to performing false intrusive attacks on the app to identify any threats or vulnerabilities before the actual hackers do. Penetration testing reveals security vulnerabilities so that necessary enhancements can be made to improve overall app security.
To implement the security steps mentioned above, the following are the top cybersecurity testing tools that can be used to test FinTech apps effectively.
Top FinTech app security Testing Tools
To implement the security steps mentioned above, the following are the top cybersecurity testing tools that can be used to test FinTech apps effectively:

Conclusion
The rising Fintech market is taking a leap of innovation through customer-centric technologies such as open banking, voice payments, embedded finance, and more. The industry also experienced an accelerated adoption due to the recent pandemic. As FinTech services providers offer intuitive and customer-centric services, cyberattacks are also on the rampage and pose a significant risk to FinTech apps.
FinTech businesses should ensure robust cyber security measures by leveraging end-to-end security testing of their apps. When the stakes for cybersecurity are higher than ever, FinTech businesses should outsource security testing to a reliable outsourcing partner to ensure thorough testing and protection of their businesses against destructive cyber-attacks.
How Can TestingXperts Help?

TestingXperts (Tx), a next-gen specialist QA & software testing company, has been helping clients from the FinTech domain with a range of testing services. Our professional team of Certified Ethical Hackers (CEHs) ensures that FinTech apps are secure from cyber vulnerabilities and meet critical security requirements such as authentication, confidentiality, and integrity. Teams have 10+ years of expertise in assessing FinTech applications for security issues and ensuring end-to-end application testing for all possible vulnerabilities.
Our Differentiators:
• A talented pool of Certified Ethical Hackers (CEHs) with years of expertise in delivering security testing services
• Flexible engagement models to meet customer’s business needs
• In-house security testing accelerator Tx-Secure makes security testing quicker, seamless, and result-oriented
• Well-equipped security testing labs where QA engineers perform effective security testing for all applications, including Blockchain, IoT, etc.
• Conformance with key industry standards such as GDPR, HIPAA, PCI-DSS, and OWASP
• Detailed test reports delivered to stakeholders for informed decisions
Discover more
Get in Touch
Stay Updated
Subscribe for more info