
Content
- An Overview of Dynamic Application Security Testing
- Importance of DAST
- How does DAST Work?
- What Business Problems Does DAST Solve?
- DAST – A Key Pillar to App Security
- Conclusion
- How TestingXperts Helps Businesses with Security Testing?
An Overview of Dynamic Application Security Testing

Dynamic Application Security Testing (DAST) is an automated security testing technique used to detect and identify vulnerabilities in applications. It is a black box testing technique that examines the application from the outside without having access to its source code or internal architecture. DAST sends malicious requests to the application and then analyzes the responses for potential vulnerabilities.
The goal of DAST is to uncover security flaws that attackers could exploit, such as Cross-Site Scripting (XSS), SQL injection, and insecure authentication mechanisms. By finding these issues early in the development process, organizations can take steps to prevent them from becoming major security incidents later on.
Importance of DAST

DAST is essential for organizations to protect their applications from malicious attacks and data breaches. DAST can detect vulnerabilities like SQL injection, cross-site scripting, and buffer overflows. It can also detect weaknesses in authentication and authorization mechanisms and insecure configurations that could lead to unauthorized access or data leakage.
By leveraging DAST, organizations are able to uplift their existing security strategy because it helps identify potential weaknesses before attackers exploit them. Organizations can proactively scan for vulnerabilities and reduce the risk of data breaches and other security incidents. Moreover, DAST can help organizations comply with various industry regulations and standards that require regular security assessments of web applications and services.
How Does DAST Work?
The typical DAST process involves scanning applications for vulnerabilities using automated tools or manual techniques. Automated tools are typically used to detect common flaws quickly and accurately, while manual methods are used to identify more complex issues. The results of these scans can then be analyzed, and the appropriate steps are taken to mitigate any identified risks.
Once the scan is complete, it is essential to review the results carefully to understand the scope of the issue and determine what action should be taken to address it. This may include patching vulnerable code, implementing additional security controls, or introducing additional training for developers and administrators. It is also essential to periodically re-scan applications to ensure that any new vulnerabilities have been identified and addressed appropriately.
What Business Problems Does DAST Solve?

DAST helps businesses protect their applications from cyber threats by identifying weaknesses that attackers could exploit. DAST can also help organizations comply with industry regulations, such as PCI DSS or HIPAA, which require specific security measures for web applications. Additionally, DAST can provide valuable insights into an organization’s overall security posture and help them make informed decisions about protecting their data and systems.
By scanning for known vulnerabilities and malicious activity, DAST can help businesses detect and respond to cyber threats before they cause significant damage. It can also provide visibility into areas of risk that may need to be identified through traditional security measures. Finally, using DAST can reduce the time required to investigate potential breaches since it will already determine potential risks before they become actual problems.
How Does DAST Differ from Other Security Testing Methods?
DAST is different from other security testing methods, such as Static Application Security Testing (SAST), which analyzes the source code of an application to identify any potential issues. DAST is also distinct from penetration testing, which attempts to exploit known vulnerabilities to gain access to sensitive information or resources.
Unlike SAST, DAST does not require access to the source code or knowledge of the application’s architecture to perform tests. Instead, it relies on scanning the application while running to detect any potential vulnerabilities.
This makes DAST ideal for web-based applications, as it can be used without requiring access to the underlying infrastructure or codebase. Additionally, DAST can be used to quickly identify newly introduced vulnerabilities that may have been missed during earlier stages of development.
DAST – A Key Pillar to App Security
Dynamic Application Security Testing (DAST) is a critical pillar in application security because it helps identify vulnerabilities in web applications by simulating attacks on running applications. DAST is an essential component of the software development lifecycle, helping to ensure that applications are secure and can withstand attacks from malicious actors.
Here are some of the reasons why DAST is considered a key pillar in application security:
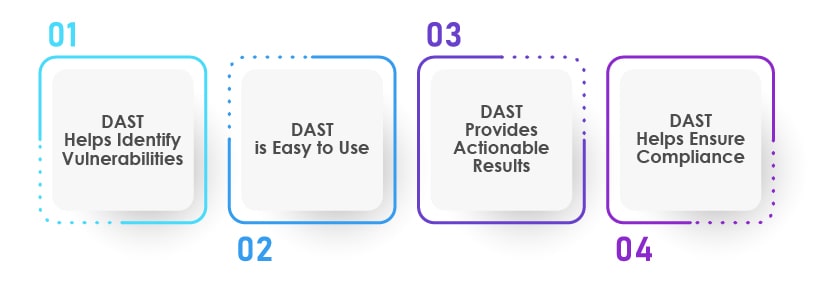
DAST Helps Identify Vulnerabilities:
DAST tools are designed to simulate real-world attacks on web applications, which helps identify vulnerabilities that attackers can exploit. Security teams can detect security weaknesses and prioritize their remediation efforts by running DAST scans.
DAST is Easy to Use:
DAST tools can be easily integrated into the software development lifecycle, making them an accessible and effective solution for identifying vulnerabilities.
DAST Provides Actionable Results:
DAST tools provide actionable results that can be used to remediate vulnerabilities quickly. These results often include detailed information about the vulnerability, including how it can be exploited, as well as recommendations for how to fix the issue.
DAST Helps Ensure Compliance:
Many compliance regulations, such as PCI DSS, require organizations to perform regular security testing on their web applications. DAST is an effective way to meet these compliance requirements and ensure that web applications are secure.
Conclusion
In conclusion, DAST is a key pillar in application security because it helps identify vulnerabilities in web applications, is easy to use, provides actionable results, and helps ensure compliance with regulations. Organizations can better protect their web applications from security threats by using DAST as part of an overall application security strategy.
How TestingXperts Helps Businesses with Security Testing?

TestingXperts (Tx) is one of the Top 5 pure-play software testing services providers globally. Tx has been chosen as a trusted QA partner by Fortune clients and ensures superior testing outcomes for its global clientele. We have rich expertise in enabling end-to-end testing services for global clients across various industry domains like healthcare, telecom, BFSI, retail & eCommerce, etc.
With our domain knowledge and with over a decade of pure play testing experience, the company has been serving the global clientele with high-quality next-gen testing services to deliver superior solutions to clients.
Our team of Certified Ethical Hackers (CEHs) ensures that your application is secure from vulnerabilities and meets the stated security requirements, such as confidentiality, authorization, authentication, availability, and integrity. Teams have more than ten years of expertise in assessing various applications for security threats and ensuring rigorous application testing for all possible threats and vulnerabilities.
TestingXperts Test Center of Excellence (TCoE) has developed Tx-PEARS –’ A holistic framework for enabling non-functional testing requirements quickly and effectively in one go. Tx-PEARS stands for Performance Engineering, Accessibility, Resiliency, & Security – Delivers innovative services in managing Non-Functional Requirements (NFRs) that help customers drive better value for their businesses with scalable and robust solutions enabling great CX.
Benefits for Businesses Leveraging Tx-PEARS
• 80-90% time saved during the planning phase as ready-to-use accelerators embedded in Tx-PEARS framework helps to jumpstart testing engagements.
• Conformance with international standards and compliance, such as GDPR, HIPAA, PCI-DSS, OSSTMM, OWASP, SANS, NIST, and others.
• Provides scalability and resiliency to applications deployed on the cloud and on-premise.
• Proactively addresses application NFRs and covers both application and infrastructure stack.
• Less code to develop and maintain as accelerators have all the required features for ensuring quicker testing outcomes.
• Helps to analyze application architecture and design to identify potential fault areas and recommend the right design patterns (e.g., circuit breakers, bulkheads, etc.)
• Executes resilience validations to understand application and infrastructure resilience.
• Analyzes monitoring and operational processes and suggests modifications to improve resilience (build self-detecting and self-healing capabilities).
• Provides Application Performance Capacity Management and Production Stability Improvement services in one go.
• Ensures equal access to apps for all people, including people with disabilities like color blindness, motor impairment, mobility impairment, etc.
• Helps to build quality gates from an NFT perspective.
• Helps in enabling an application to be fault-tolerant, reduce latency, and make it load tolerant.
• Ensures business continuity even during sub-system/component failures.
• Helps to cut down QA costs by 40%.
• Save around 55% on the total cost of ownership
Discover more
Get in Touch
Stay Updated
Subscribe for more info




