An Overview of the Digital Immune System

In today’s digital age, our reliance on technology has increased significantly. As a result, the threat landscape has also evolved. Just as our bodies have an immune system to protect us from viruses and other harmful intruders, our digital world needs a similar defense mechanism. This is where the concept of a digital immune system comes in.
One of the main aspects of a digital immune system is a collection of security technologies and processes that work together to detect, prevent, and respond to cyber-attacks. Similar to how our immune system adapts to new threats and develops immunity, a digital immune system uses machine learning and artificial intelligence to analyze data and learn from previous attacks to improve its defenses. It is an essential component of any organization’s digital defense strategy, helping to safeguard sensitive data and critical infrastructure.
The digital immune system comprises several layers of defense, starting from the network perimeter and extending to the core of the system. It includes various security mechanisms such as firewalls, intrusion detection and prevention systems, antivirus software, and security information and event management systems. These security mechanisms work together to monitor and analyze network traffic, detect suspicious activity, and prevent or mitigate potential threats.
Why Are Digital Businesses in Need of Digital Immunity?

As businesses increasingly rely on digital technologies to run their operations, they are exposed to a growing array of cyber threats. Hackers, cybercriminals, and other bad actors are constantly developing new methods to breach digital defenses and steal valuable data, disrupt operations, or cause other forms of harm. In this context, digital immunity refers to the ability of a business to protect itself from these threats and maintain its operations even in the face of attacks.
Digital immunity is particularly important for digital businesses, which rely on digital technologies to deliver their products and services. These businesses are often more vulnerable to cyber threats than traditional brick-and-mortar companies, as they have more digital touchpoints with customers and store valuable data in digital formats.
To achieve digital immunity, businesses need to implement a range of measures to protect their digital assets and operations. This can include implementing strong passwords and access controls, using encryption to protect sensitive data, regularly updating software and systems, monitoring networks for suspicious activity, and training employees on how to identify and respond to cyber threats.
Evidently, achieving digital immunity is a critical priority for digital businesses that want to protect themselves from the growing array of cyber threats in today’s digital landscape. By taking a proactive approach to cybersecurity, these businesses can help ensure their long-term success and protect their customers’ trust and privacy.
Significance of Digital Immune Systems
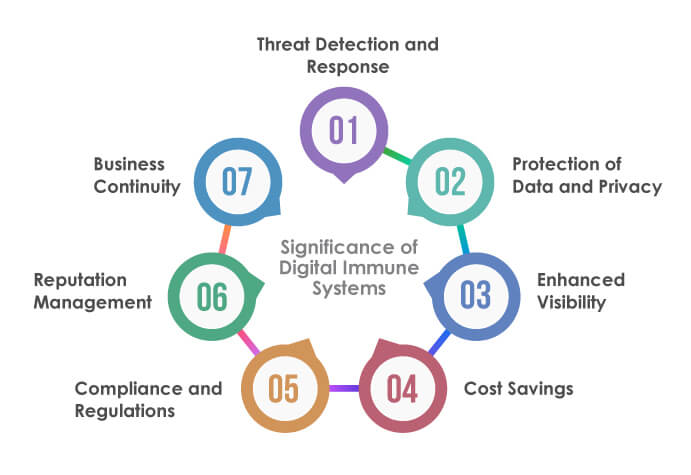
Here are the key significance of digital immune systems:
Threat Detection and Response:
Digital immune systems are crucial in detecting cyber threats and providing immediate responses to them. By analyzing network activity and user behavior, these systems can quickly identify and mitigate threats, preventing further damage to systems and data.
Protection of Data and Privacy:
Digital immune systems help protect sensitive data by monitoring all activity across the network and identifying unusual behavior. This ensures that data is secure and not accessed by unauthorized individuals.
Enhanced Visibility:
With digital immune systems, organizations have increased visibility into their network, providing valuable insights into security threats and risks. This allows for proactive measures to be taken to prevent attacks before they occur.
Cost Savings:
Digital immune systems can save organizations significant amounts of money by preventing cyber-attacks and reducing the costs associated with remediation efforts.
Compliance and Regulations:
With the increasing number of regulations around data privacy and security, digital immune systems are necessary for organizations to comply with these regulations. These systems help organizations avoid costly fines and reputational damage that can result from non-compliance.
Reputation Management:
In the digital age, reputation is everything. Digital immune systems help organizations protect their reputation by detecting and responding to threats before they can do damage to an organization’s reputation.
Business Continuity:
Cyber-attacks can result in significant downtime for organizations, leading to lost revenue and productivity. Digital immune systems help ensure business continuity by preventing attacks and quickly responding to any incidents that do occur.
Digital immune systems play a critical role in protecting organizations from cyber threats. By providing threat detection and response, protecting data and privacy, enhancing visibility, and saving costs, these systems are essential for any organization looking to protect itself in the digital age.
Setting up a Digital Immune System – Key Considerations
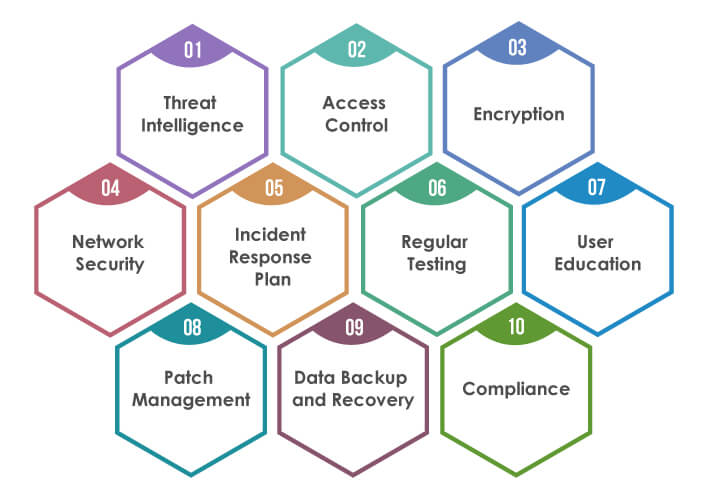
As technology evolves, the need for organizations to establish a digital immune system becomes increasingly important. Hence, it is crucial for organizations to consider the following key considerations while setting up their digital immune system:
Threat Intelligence:
An effective digital immune system should have a solid threat intelligence system that identifies and analyzes potential threats to digital assets.
Access Control:
Organizations need to ensure that access to digital assets is granted only to authorized personnel. This involves implementing multi-factor authentication, password policies, and role-based access control.
Encryption:
Encryption is a critical component of a digital immune system as it ensures that data transmitted and stored is secure and protected from unauthorized access.
Network Security:
The organization’s network must be secure to prevent malicious actors from accessing it. This can be achieved by implementing firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and network segmentation.
Incident Response Plan:
The organization should have a well-defined incident response plan that outlines the procedures to follow in case of a security breach or cyber-attack.
Regular Testing:
Organizations should regularly test their digital immune system to identify any weaknesses or vulnerabilities. This can be done through penetration testing, vulnerability scanning, and security assessments.
User Education:
Organizations should educate their employees on security best practices to prevent them from inadvertently exposing the organization to cyber threats.
Patch Management:
It is essential to keep all software and systems up-to-date with the latest security patches to address known vulnerabilities.
Data Backup and Recovery:
A digital immune system should have a robust data backup and recovery system that ensures the organization can recover from a cyber-attack or breach.
Compliance:
Organizations need to ensure that their digital immune system complies with relevant regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA).
A robust digital immune system is essential for organizations to protect their digital assets from cyber threats and attacks. The above key considerations are crucial for organizations to consider while setting up their digital immune system. By implementing these measures, organizations can minimize the risk of a security breach or cyber-attack and safeguard their digital assets.
Key Aspects of a Digital Immune System
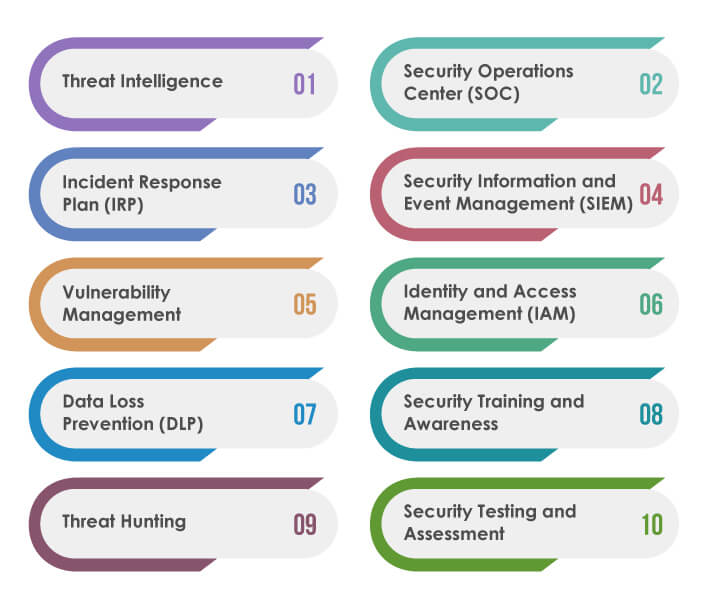
A digital immune system is a set of technologies, processes, and protocols designed to protect digital assets from cyber threats. Some key aspects of a digital immune system include:
Threat Intelligence:
The ability to gather and analyze data from various sources to identify potential threats and vulnerabilities.
Security Operations Center (SOC):
A centralized unit responsible for monitoring, detecting, analyzing, and responding to security incidents.
Incident Response Plan (IRP):
A pre-defined set of procedures and protocols to follow in the event of a security breach.
Security Information and Event Management (SIEM):
A system that collects and analyzes security-related data from multiple sources to detect and respond to potential security incidents.
Vulnerability Management:
A process of identifying, prioritizing, and addressing vulnerabilities in software, hardware, and networks.
Identity and Access Management (IAM):
A framework of policies and technologies that ensure only authorized users have access to digital assets.
Data Loss Prevention (DLP):
A set of technologies and policies that prevent the loss or theft of sensitive data.
Security Training and Awareness:
Ongoing education and training programs for employees to promote good security hygiene and awareness.
Threat Hunting:
Proactive searching for potential security threats in digital assets and networks.
Security Testing and Assessment:
Regular testing and assessment of the effectiveness of security measures and processes.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a digital immune system is a critical defense mechanism that helps organizations proactively identify and respond to cyber threats. As cyber threats continue to evolve and become more sophisticated, having a robust digital immune system in place is becoming increasingly important. By leveraging advanced technologies such as machine learning and artificial intelligence, organizations can better detect and respond to potential threats before they cause significant damage. As we move forward into an increasingly digital age, it is crucial for organizations to prioritize the development and implementation of a strong digital immune system to protect their critical assets and data.
Discover more
Stay Updated
Subscribe for more info