
- What is Data Migration?
- Common Data Migration Challenges
- Techniques to Overcome Data Migration Challenges
- Implementing Data Migration Testing
- Best Practices in Data Migration Testing
- Conclusion
- Why Partner with TestingXperts for Data Migration Testing?
Data migration, a critical business process, involves transitioning data from one storage system, database, application, or server to another. This frequent yet challenging task is essential for modern organizations, especially with the growing trend of moving data to the cloud. Despite cloud spending accounting for less than 20% of the overall IT market, its growth rate outruns other areas significantly.
Addressing these challenges is crucial to avoid data loss, which can occur when parts of data aren’t transmitted correctly during migration. Moreover, semantic errors can lead to inaccurate reporting and data gaps, while extended downtime during migration might result in significant business losses.
The complexity of data migration demands a robust testing strategy. This ensures data integrity and security and maintains continuity and efficiency in business operations. The potential risks of data migration, such as data corruption, application performance issues, and data orchestration complexities, can be mitigated with the right approach.
What is Data Migration?
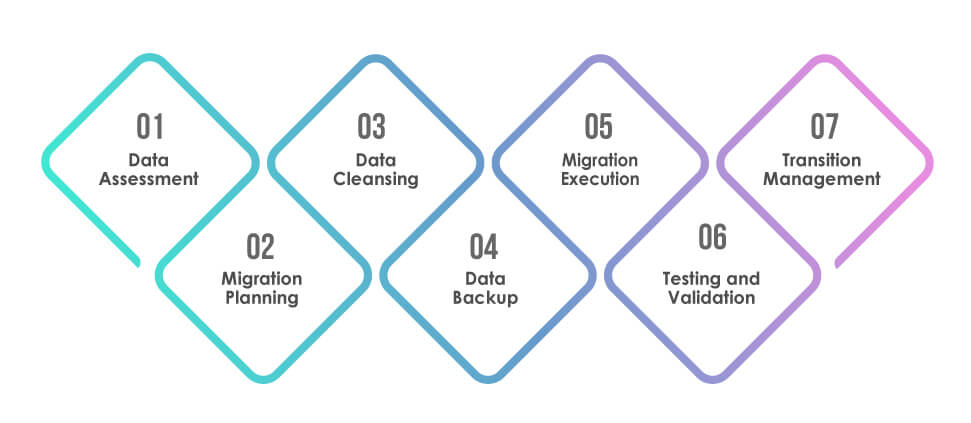
Data migration is the process of transferring data from one system to another. While this might sound simple, it involves a complex interplay of various elements to ensure data integrity, security, and accessibility in the new environment. The process typically moves data from legacy or outdated systems to modern, efficient platforms, often driven by the need for better data management and analysis capabilities. Some of the key components of data migration are
Data Assessment
The initial step is thoroughly examining the existing data. It involves understanding the data format, volume, and quality. Assessing data helps identify inconsistencies or redundancies that could affect the migration process.
Migration Planning
This critical phase outlines the strategy for migration. It encompasses defining goals, choosing appropriate migration tools, allocating resources, and setting realistic timelines. Effective planning also involves identifying risks and developing contingency plans.
Data Cleansing
Before migration, data must be cleaned and standardized. This process involves correcting errors, removing duplicates, and ensuring data consistency. Clean data not only simplifies the migration process but also enhances the value of the data in the new system.
Data Backup
Creating backups is essential to safeguard against data loss during migration. This step ensures that data can be restored to its original state in case of unforeseen issues.
Migration Execution
Transferring data from the source to the target system. It needs to be meticulously executed to preserve data integrity and order. Data is transformed and adapted during this phase to fit the new system’s requirements.
Testing and Validation
Rigorous testing ensures data accuracy and integrity after migration. This phase checks for the new system’s data completeness, accuracy, and functionality. It is crucial to confirm that the migration meets all predefined objectives.
Transition Management
The final phase involves smoothly transitioning from the old to the new system. This requires careful management to minimize disruption to ongoing business operations. It often involves training users on the new system and gradually phasing out the old one.
Common Data Migration Challenges

The data migration process can be challenging despite its critical importance in modern business operations. These obstacles can affect the migration process if not properly managed, resulting in significant setbacks and inefficiencies. Understanding these challenges is the first step in mitigating their impact and ensuring a successful migration.
Data Quality Issues
Data quality is crucial in migration projects. Common issues include duplicate records, missing values, and outdated information. These quality problems can disrupt business processes, lead to incorrect decision-making, and undermine the integrity of the new system. Ensuring high-quality data involves comprehensive audits, cleansing procedures to remove inaccuracies, and validation processes to verify data accuracy and consistency. Effective data quality management requires a blend of automated tools and manual oversight to ensure the data migrated is reliable and useful for business operations.
Data Loss and Corruption
The risk of data being lost or corrupted during migration is a significant concern. This can occur due to various factors, such as technical failures, human errors, or compatibility issues between old and new systems. Robust backup and recovery procedures must be in place to mitigate this risk. This includes regular data backups before and during migration, rigorous testing to ensure data integrity, and establishing fail-safes to restore data quickly in case of loss or corruption. Monitoring data continuously throughout the migration is crucial to promptly detect and address any issues.
Incompatibility Between Systems
Migrating data between systems with different architectures, formats, or functionalities can lead to significant challenges. This incompatibility can result in data being misrepresented, lost, or rendered unusable in the new system. Addressing this requires a detailed analysis of the source and target systems to identify potential compatibility issues. Effective strategies include data transformation processes to align data formats, developing custom scripts to bridge functionality gaps, and thorough testing to ensure seamless integration between systems.
Lack of Proper Planning
Inadequate planning is a major pitfall in data migration projects. This encompasses underestimating the complexity of migration, failing to allocate sufficient resources, or overlooking critical steps in the migration process. Comprehensive planning should involve stakeholder engagement, defining clear objectives and scope, detailed resource allocation, timeline development, and contingency planning. This phase should also include identifying potential risks and devising mitigation strategies. Monitoring and adjustments throughout the migration process are essential to ensure alignment with the initial plan.
Security and Compliance Risks
Data migration often involves handling sensitive or regulated data, posing significant security and compliance risks. Breaches during migration can lead to data exposure, legal penalties, and reputational damage. Compliance with data protection regulations (like GDPR) and implementing robust security measures are crucial. This involves encrypting data during transit and at rest, conducting security audits, and ensuring the new system complies with all relevant regulatory requirements. Additionally, staff training on data handling best practices and regular reviews of security protocols are essential to maintain data integrity and compliance.
Techniques to Overcome Data Migration Challenges
Successfully comprehending the complexities of data migration requires strategic techniques. These methods not only address common challenges but also enhance the efficiency and security of the migration process. Organisations can mitigate risks and ensure a smooth transition to the new system by adopting a comprehensive approach.
Ensuring Data Quality and Integrity
To ensure successful data migration, it’s crucial to maintain high data quality and integrity. This involves thorough data cleansing to remove inaccuracies and duplications, data validation to ensure correctness and consistency, and regular data audits to assess data quality continuously. By addressing these aspects, businesses can mitigate the risk of migrating poor-quality data, which could lead to decision-making errors and operational inefficiencies in the new system.
Addressing System Compatibility
One of the key challenges in data migration is ensuring compatibility between the old and new systems. This includes aligning data formats, structures, and functionalities. Compatibility assessment and employing data transformation tools are vital to adapting data to the new system’s requirements. This process might involve converting data into different formats, restructuring databases, or customising software solutions to bridge functionality gaps, ensuring seamless data integration and functionality in the new environment.
Data Backup and Recovery Strategies
Robust data backup and recovery strategies are essential to safeguard against data loss or corruption during migration. This includes regular data backups before and during migration and establishing effective recovery mechanisms. These strategies ensure that, in case of any disruptions or data integrity issues during the migration, there is a reliable method to restore the original data quickly, minimising the risk of data loss and ensuring business continuity.
Securing Data During Migration
Data security is paramount, especially when handling sensitive or regulated data. This technique involves implementing strong encryption for data in transit and at rest, using secure data transfer protocols, and conducting regular security audits to identify and rectify vulnerabilities. Compliance with data protection regulations, such as GDPR, is also essential to prevent breaches and ensure legal compliance. A comprehensive security approach during migration protects data from unauthorised access and potential breaches.
Stakeholder Communication and Training
Effective stakeholder communication and training are critical for the success of data migration projects. Keeping all stakeholders informed and engaged throughout the migration process ensures alignment and reduces the likelihood of misunderstandings or errors. Training staff using the new system is equally important to facilitate a smooth transition and adoption. This involves educating them about new processes and functionalities, which helps minimise disruptions and enhance the migration process’s overall efficiency.
Implementing Data Migration Testing
Types of Testing
Unit Testing
This type of testing focuses on individual units or components within the data migration process. It’s about testing each field, record, or function separately to ensure they work correctly in isolation. This level of testing is crucial for identifying specific errors or issues that might not be apparent in a broader testing context.
System Testing
System testing evaluates the complete migrated system’s functionality. It checks if the system operates as expected once the data is migrated. This testing phase is essential for verifying that all aspects of the system including hardware, software, and data – interact correctly and meet the operational requirements.
Integration Testing
Integration testing assesses how well different systems and components work together post-migration. It’s essential when migrating data between systems that need to interact or depend on each other. This testing ensures that data flows seamlessly between systems and has no integration issues, such as data mismatches or communication errors.
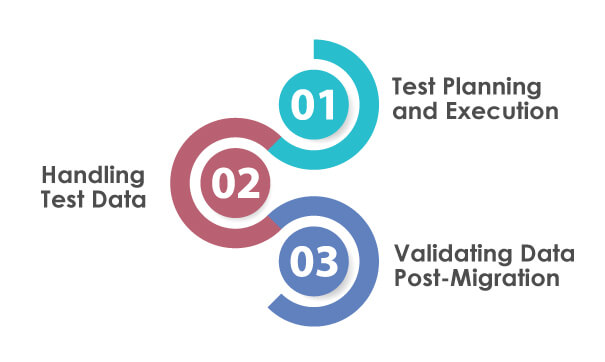
Test Planning and Execution
A detailed test plan is essential for businesses to execute their data migration strategy. This plan should outline the objectives, methodologies, tools, and criteria for successful testing. The execution phase involves implementing the program, closely monitoring the process, and documenting findings. Regular reviews and adjustments based on test results help maintain the migration process’s effectiveness.
Handling Test Data
Effective test data management involves creating realistic data sets that mimic actual data to be migrated. This includes ensuring data diversity to cover all possible scenarios and maintaining data security and privacy during testing. Test data should represent real-world usage to ensure the validity of the testing process.
Validating Data Post-Migration
After migration, it’s critical to validate the data to ensure it has been transferred accurately and functions correctly in the new environment. This involves comparing migrated data with the source data for consistency, verifying data integrity, and ensuring that all functionalities are operational. Successful validation signifies that the migration process has achieved its intended goals.
Best Practices in Data Migration Testing
Data migration testing is a critical phase in the data migration process, ensuring the data’s accuracy, integrity, and performance. Adhering to best practices in this phase mitigates risks and contributes to the overall success of the migration. These practices help identify and address potential issues early, ensuring a seamless transition.
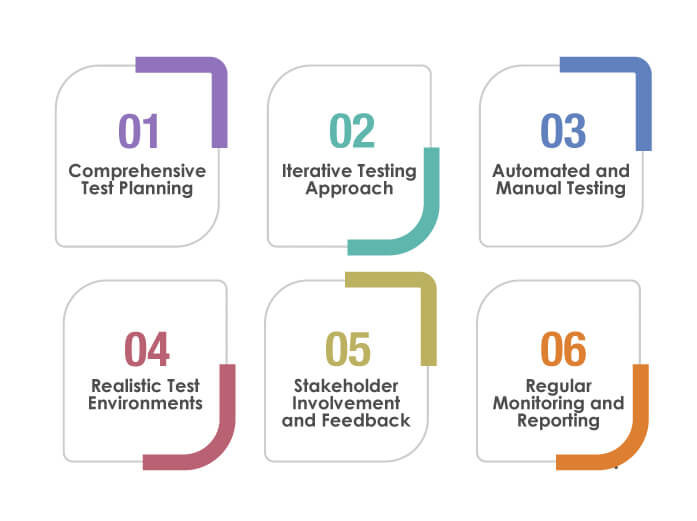
Comprehensive Test Planning
A detailed test plan is the backbone of effective data migration testing. It should clearly define what needs to be tested, how it will be tested, and the expected outcomes. This plan must also include specific criteria for data validation, risk assessment, and handling of potential issues. A thorough plan guides the testing team and ensures business objectives and technical requirements are aligned.
Iterative Testing Approach
An iterative approach allows for continuous improvement and adaptation. Start with small-scale tests to identify and address major issues early, then progressively expand the scope to more complex and larger data sets. This method enables the team to refine their testing strategy and tools, ensuring better coverage and more accurate results.
Automated and Manual Testing
Leverage the potential of both automated and manual testing. Automation increases efficiency, particularly for large volumes of data and repetitive tests. At the same time, manual testing provides the flexibility to explore specific scenarios and complex data relationships that automated processes might not cover.
Realistic Test Environments
Simulating the production environment as closely as possible in the test environment is crucial. This includes mirroring data, configurations, and system interactions. Such environments help uncover issues that might only appear under production-like conditions, ensuring a more reliable migration.
Stakeholder Involvement and Feedback
Regular engagement with stakeholders, including end-users, IT staff, and business leaders, provides critical insights. Their feedback on test results can uncover practical issues and usability challenges, offering a more comprehensive view of the migration’s effectiveness.
Regular Monitoring and Reporting
Continuous testing process monitoring helps identify trends, track progress, and promptly address issues. Regular reporting to all stakeholders keeps the process transparent and ensures that everyone is informed about the status and outcomes of the testing phase.
Conclusion
Effective data migration testing is fundamental to the success of any data migration project. Organizations can significantly enhance the accuracy and efficiency of their data migration processes by implementing best practices such as comprehensive planning, iterative testing, balanced automation and manual testing strategies, realistic test environments, stakeholder engagement, and continuous monitoring. These practices help mitigate risks, ensure the migrated data aligns with business needs, and maintain its integrity and usefulness. As data continues to be a crucial asset for businesses, the importance of thorough data migration testing cannot be overstated.
Why Partner with TestingXperts for Data Migration Testing?

At TestingXperts, we are committed to delivering top-notch data migration testing services. Our expertise, customized approach, comprehensive solutions, and uncompromising focus on security and compliance set us apart, making us the ideal partner for your data migration needs.
• Our team of data migration testing experts can handle complex data migrations, ensuring a seamless transition for your business.
• We utilise the latest tools like Query Surge, for which we are the platinum partners and technologies to ensure your data is accurately migrated and retains its integrity and functionality in the new system.
• Our in-house accelerators and customized solutions are designed to meet your needs and requirements, providing personalized service that adds value to your project.
• We implement rigorous testing processes to ensure that every piece of data is correctly migrated and fully operational.
• Understanding the importance of data security, we adhere to the highest security and compliance standards. Our testing protocols are designed to protect your data throughout the migration process.
• Our in-house Tx-Automate is seamlessly integrated with data migration tools, empowering it to perform end-to-end validation of dashboards and ensuring consistency from the front end to the back end of the database.
Contact our QA experts now to know more about our data migration testing services.
Discover more
Get in Touch
Stay Updated
Subscribe for more info




