
The retail industry is particularly vulnerable to cybercrime due to the vast amounts of personal and financial data that retailers store and process. Cybercriminals can use a variety of tactics such as payment card fraud, point-of-sale malware, phishing, and DDoS attacks to steal sensitive information or disrupt business operations. Retailers must take proactive measures to secure their networks and systems, including implementing strong security protocols, training employees on cybersecurity best practices, regularly updating software, and working closely with payment processors and other vendors to ensure their security standards are up to date. Failure to take cybersecurity seriously can lead to reputational damage, financial loss, and legal consequences for retailers.
Why Retail is the Top Target for Security Threats in the UK?
Retailers are a prime target for ransomware attacks, where hackers infiltrate the retailer’s network and hold their data hostage until a ransom is paid. This is particularly effective against retailers because they need to have access to customer data in order to conduct business, and any loss of this data can be extremely damaging to their reputation and bottom line.
Retailers are also susceptible to attacks through third-party vendors, who may have access to sensitive customer data. As retailers increasingly rely on third-party providers for various aspects of their business, they open themselves up to additional vulnerabilities in their supply chain.
Let’s dig into the details to understand why the retail industry is an easy target:

High volume of sensitive data:
Retailers handle a large volume of sensitive data such as customer credit card information, personal identification information, and purchase history. This data is highly valuable to cybercriminals and can be used for identity theft, financial fraud, and other malicious activities.
Multiple attack surfaces:
Retailers have multiple points of entry for cybercriminals to exploit, including online stores, mobile apps, physical stores, and supply chain partners. Each of these entry points represents a potential vulnerability that can be exploited by cybercriminals.
Limited security budgets:
Retailers often have limited security budgets and resources to invest in cybersecurity, making them an easy target for cybercriminals. They can exploit this weakness by targeting smaller retailers who may not have invested enough in cybersecurity.
Difficulty in securing legacy systems:
Retailers often have legacy systems that are difficult to secure and update. These systems may have vulnerabilities that can be exploited by cybercriminals.
Ease of monetization: Stolen credit card information and other sensitive data can be easily monetized on the dark web, making retail a lucrative target for cybercriminals.
What are the Threats to Retail Cybersecurity in the United Kingdom?
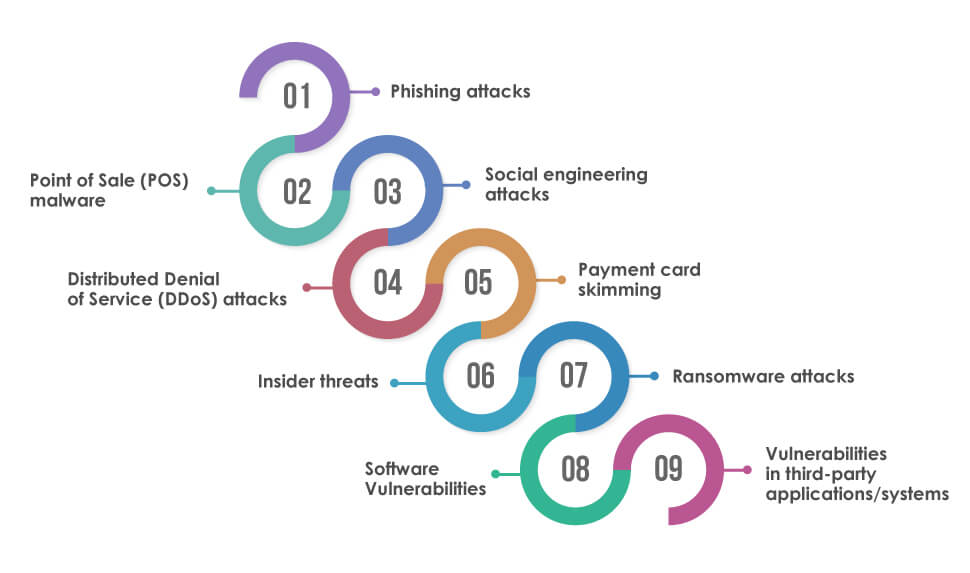
There are several potential threats to retail cybersecurity, including:
Phishing attacks:
Phishing attacks are attempts to trick users into sharing sensitive information like passwords or credit card details through fake emails or websites.
Point of Sale (POS) malware:
Malware designed to infect and compromise the software that runs on retail point-of-sale systems, allowing attackers to steal payment card data.
Social engineering attacks:
Attackers may try to trick employees or customers into revealing sensitive information or performing actions that compromise the security of the retail environment.
Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks:
DDoS attacks involve overwhelming a website or network with traffic, making it unavailable to users.
Payment card skimming:
Skimming devices can be attached to card readers to collect credit card data when customers make payments.
Insider threats:
Employees with access to sensitive data or systems may intentionally or unintentionally cause harm to the retail environment.
Ransomware attacks:
Ransomware is a type of malware that encrypts files on a victim’s computer, rendering them inaccessible until a ransom is paid.
Software Vulnerabilities:
Software vulnerabilities on the web and mobile applications like Cross Site Scripting, Injection attacks, dangerous file uploads can be used by attackers to gain sensitive information of the users of the application.
Vulnerabilities in third-party applications/systems:
Vulnerabilities in the dependent libraries and plugins can be exploited by attackers to compromise the security of the retail environment.
These threats highlight the importance of implementing strong cybersecurity measures, such as regular employee training, multi-factor authentication, encryption, and continuous monitoring and threat detection.
Simple Steps to protect your Retail Business from Cyber Threats
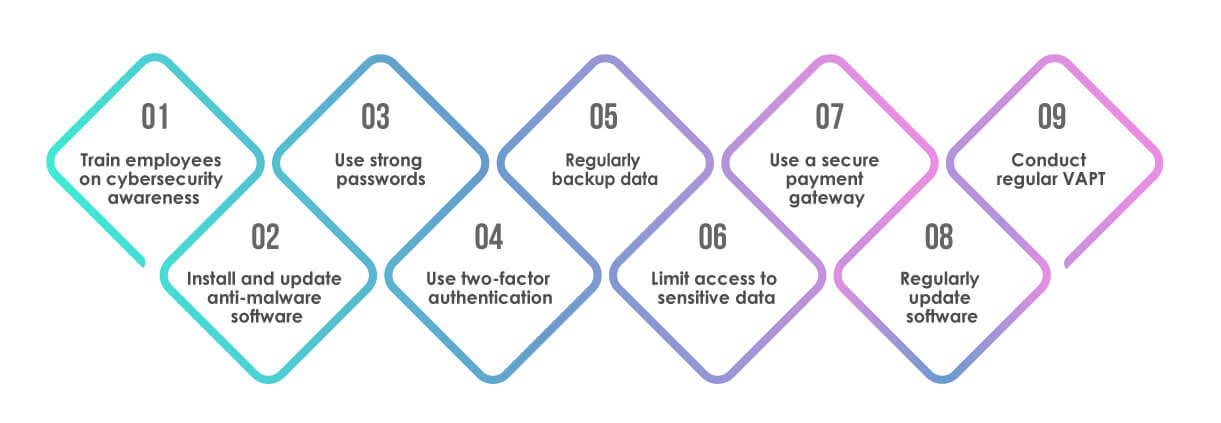
As a retail business owner, it is crucial to protect your business from cyber threats. Here are some simple steps you can take to protect your retail business from cyber threats:
Train employees on cybersecurity awareness:
It’s essential to educate your employees on cybersecurity best practices. This includes how to create strong passwords, how to spot phishing emails, and how to report any suspicious activity.
Install and update anti-malware software:
Install anti-malware software on all of your devices, including computers, laptops, and mobile devices. Ensure the software is updated regularly to protect against the latest threats.
Use strong passwords:
Make sure you and your employees use strong passwords that are difficult to guess. Use a combination of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters.
Use two-factor authentication:
Two-factor authentication provides an extra layer of security to your accounts. This requires users to enter a code sent to their phone or email, in addition to their password, to access their account.
Regularly backup data:
Regularly back up all your data, including customer data, financial records, and inventory records, to protect against data loss in case of a cyber-attack.
Limit access to sensitive data:
Only grant access to sensitive data to employees who need it to perform their job. Use different levels of access permissions to control who can access what data.
Use a secure payment gateway:
Use a secure payment gateway to protect your customers’ payment information. Choose a payment gateway that is PCI compliant and uses encryption to protect data.
Regularly update software:
Keep all software up to date, including operating systems, anti-malware software, and other applications. This ensures that any known vulnerabilities are patched and can’t be exploited by cybercriminal
Conduct regular VAPT:
Regular Vulnerability Assessment and Penetration Testing should be conducted, minimum after every six months or whenever there is a major change in the retail applications and systems.
Conclusion
Cybercrime has become a significant threat to the retail industry in the United Kingdom. The rise of online shopping has increased the opportunities for cybercriminals to exploit vulnerabilities in retailers’ digital infrastructure. The consequences of a successful cyber-attack can be severe, including reputational damage, financial losses, and legal repercussions. Therefore, retailers must take proactive measures to protect their systems and data, including implementing robust cybersecurity protocols, training employees on best practices, and staying up to date with the latest security technologies. With the right approach, retailers can minimize the risk of cybercrime and continue to thrive in an increasingly digital marketplace.
How TestingXperts can help you with Cybersecurity in Retail?

TestingXpert innovative retail software solutions assist organizations to fit better with their customer’s needs. We have experience working with the major retail industries on digital quality engineering from fashion to food to eCommerce.
ERP, warehouse management, payment systems, retail store POS software testing and the rest of the applications in the enterprise ecosystem need to work all together on today’s eCommerce platforms.
TestingXperts offers world-class eCommerce website testing solutions through UI & user testing. Those sanction the eCommerce portals and retail software testing companies to be all set for the required certification.
Need assistance?
We have our eCommerce and Retail experts in the house to talk to you about testing eCommerce websites. They will help you offer a solution for your business and will illustrate how to scale the quality needs further to create a robust eCommerce security platform catering to all your retail cybersecurity and shopping needs.
Discover more
Get in Touch
Stay Updated
Subscribe for more info




