Table of Contents
- What are Cloud-Native Applications?
- Why Lift-and-Shift Approach Doesn’t Work?
- Cloud v/s Cloud-Native Apps
- 7 Business Benefits of Cloud-Native Applications
- Summary
- How can Tx Help with Cloud-Native App Testing?
“According to a study by Gartner, cloud-Native platforms will serve as a base for more than 95% of digital initiatives by 2025.”
In today’s fast-paced digital business environment, speed, resiliency, and agility are the three factors organizations need to boost their growth and remain competitive. It’s difficult to pursue such goals without effective digital initiatives, which, in turn, ask businesses to choose cloud over on-premises solutions and modernize their existing systems. This is where cloud-native tech solutions come in – playing a significant role in building and transforming business applications to meet changing market demands. According to statistics, the market for cloud-Native applications is projected to reach $17 billion by 2028.
Businesses also acknowledge that by integrating a cloud-Native approach within their processes, they can develop and deploy software solutions faster and efficiently utilize cloud capabilities like flexibility and speed. Its role in facilitating digital transformation is another reason businesses move towards cloud computing and support hybrid and remote work models.
What are Cloud-Native Applications?
Before discussing cloud-Native applications, let us understand what “cloud-Native” means. Gartner defines cloud-native as “a solution created to leverage cloud capabilities. It includes delivering capabilities that are elastic and scalable, service-based, metered, shared, and present everywhere because of internet technologies.” Cloud-Native platforms allow businesses to optimize their cloud implementation process and improve the time-to-market of their digital initiatives.
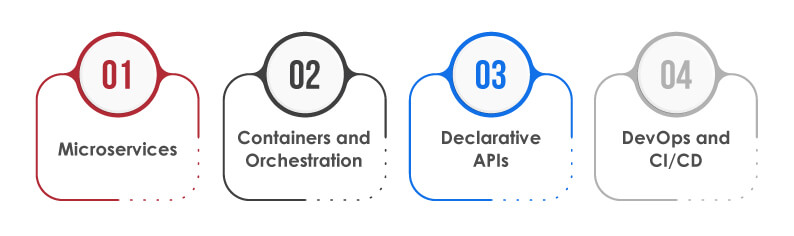
Cloud-Native applications depend on a modern approach to building and running apps to utilize cloud computing’s full benefits. These apps are specifically built for cloud environments and are scalable, flexible, and easy to deploy across various cloud infrastructures. Its key components include:
Microservices:
Cloud-Native apps are a collection of small, independent services known as microservices. It allows each application part to be independently developed, deployed, and scaled. This, in turn, improves agility and reduces development and maintenance complexity.
Containers and Orchestration:
Containers consist of microservices to make apps portable across varying cloud environments. Tools like Kubernetes orchestrate these containers to ensure they run and scale as per business requirements.
Declarative APIs:
Cloud-Native applications facilitate immutable infrastructure where changes are done by replacing components. Declarative APIs specify the desired state of the application, allowing the system to maintain that state automatically.
DevOps and CI/CD:
Cloud-Native apps are developed using DevOps practices. It involves using CI and CD processes to frequently and automatically update applications, reducing time-to-market and facilitating rapid response to market or customer demands.
Why Lift-and-Shift Approach Doesn’t Work?
A popular approach in cloud migration services includes rehosting existing applications and their data in the cloud with minimum changes. This approach is “lift-and-shift,” meaning lifting apps from the premises infrastructure and ‘shifting’ to the cloud hosting environment. Although this approach is quick and straightforward, this method is not enough to reap the full benefits of cloud computing.
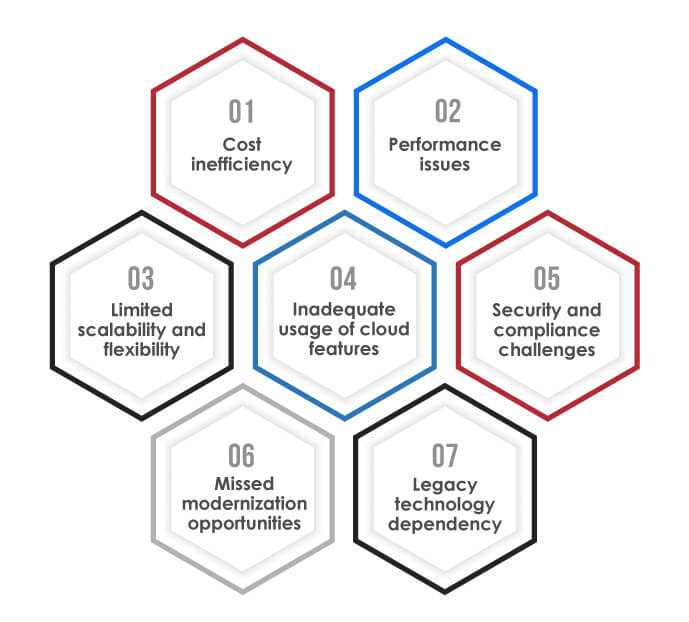
Applications will not work as intended in the cloud, and the adjustment will also require time, manual resources, and significant investment. Certain bottlenecks also force businesses to give up on the scalability and performance of the cloud environment. Businesses must realize that migrating aging systems to the cloud is insufficient to stay competitive and offer quality services at the same time, in today’s digital age. Following are some of the limitations of the lift-and-shift approach:
• Cost inefficiency
• Performance issues
• Limited scalability and flexibility
• Inadequate usage of cloud features
• Security and compliance challenges
• Missed modernization opportunities
• Legacy technology dependency
Cloud v/s Cloud-Native Apps

| Features | Cloud | Cloud-Native |
| Architecture | Based on a traditional architecture that does not fully leverage cloud functionalities. | Specifically built for cloud environments and utilizes microservices architecture. |
| Deployment | Involves lifting and shifting existing apps to the cloud. | Applications are developed specifically for cloud deployment by using cloud-specific tools and services. |
| Scalability | Easy to upscale but requires manual intervention, and scaling is limited due to application design. | Highly scalable and automatically adjusts to load changes using cloud features like auto-scaling. |
| Cost Efficiency | May incur high costs due to overprovisioning or underutilization of resources. | Cost-efficient solution with optimal resource utilization and follows a pay-as-you-go pricing model. |
| Performance | Performance depends on the app’s original design and is difficult to optimize for a cloud environment. | Optimized for high performance in a cloud environment, utilizing advanced cloud technologies and distributed computing. |
| Flexibility and Adaptability | The app’s original environment and design limit the flexibility. | Highly flexible and adapts to changing needs because of the modern design approach. |
| Security | Security protocols should sync with the cloud, and there is a chance of vulnerabilities. | Designed using modern security practices like DevSecOps to enhance cloud security. |
| Updates and Maintenance | Challenging and time-consuming and requires more traditional IT management. | DevOps practices like CI/CD simplify the updation and maintenance process. |
| Innovation Potential | Limited due to existing technology and architecture constraints. | Uses cutting-edge cloud technologies for rapid deployment capabilities. |
| Integration with Cloud Services | Integration is possible but will not be seamless or fully optimized. | Seamless integration with varying cloud services and APIs for enhanced functionality. |
7 Business Benefits of Cloud-Native Applications
Cloud-native applications offer various business benefits to help them stay competitive and agile in the dynamic digital environment. Some of the benefits are given below:
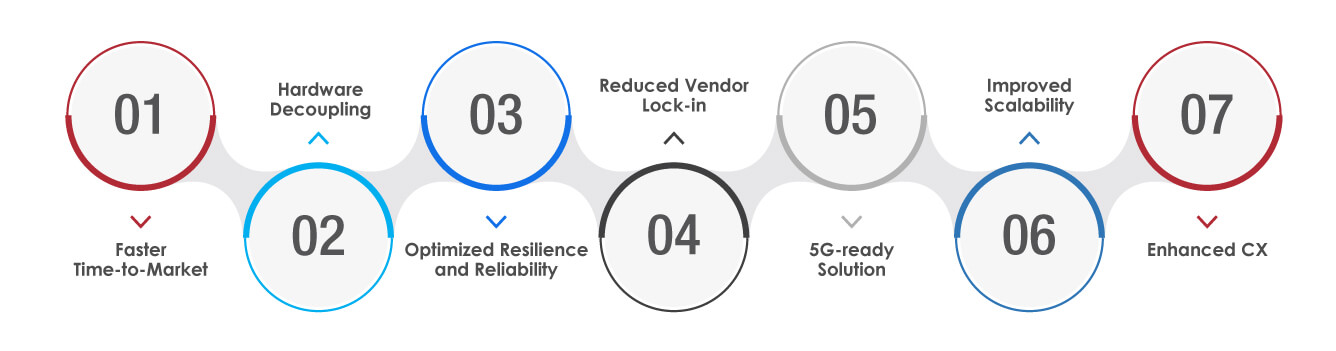
Faster Time-to-Market:
Time-to-market is one of the key differentiators between businesses that are planning to grow and remain competitive in the digital age. The faster they can build and deliver value to their users, the higher the chances of success and low business disruption. Modern DevOps practices use automation to transform the software delivery pipeline by making it faster and more predictable. Cloud-Native apps support DevOps practices to enable automation and collaboration, which is not supported in local development and limited server-based delivery processes.
Hardware Decoupling:
Cloud-Native tech offers decoupling from hardware, facilitating adaptability and flexibility. These apps can run on commodity hardware, enterprise-grade servers, and public clouds. Cloud-Native apps are dependent only on the container runtime environment.
Optimized Resilience and Reliability:
Cloud-Native apps use microservices architecture to ensure that a single component failure doesn’t affect the entire system. This results in a rise in uptime and reliability, necessary for business continuity and maintaining user trust.
Reduced Vendor Lock-in:
Selecting the right cloud vendor who offers security, maintenance, and performance is important. However, the chances of poor service quality and high pricing plans are integral to traditional app development, where businesses have to stick to the same cloud vendor due to time and resource constraints. However, cloud-Native app development mitigates vendor lock-in issues by enabling businesses to use services from multiple cloud vendors. Businesses can easily shift to the vendor with better cloud pricing and benefits.
5G-ready Solution:
Individuals have started to adopt 5G for better accessibility worldwide, with organizations focusing on adapting to modern and faster technologies. Cloud-Native apps rely on faster internet for swift responses, and businesses can hop on board the decades of development that better technologies are yet to bring.
Improved Scalability:
Cloud-Native applications are highly scalable and can handle varying workloads by dynamically allocating resources according to current demand. This flexibility is necessary for businesses that experience fluctuating traffic spikes or those going through digital transformation or scaling their operations.
Enhanced CX:
Customer experience is a crucial aspect of every business. E2E, cloud-specific app development facilitates a seamless connection between a smooth CX and app functionality. Also, cloud-Native application development involves customers for rapid feedback and efficient deployment of new updates.
Summary
Speed, resilience, and agility are the key factors for businesses aiming to grow and stay competitive, and cloud-Native technology is a vital component in this context. It involves gearing businesses with the necessary tools to adapt and innovate in the evolving market. Cloud-Native applications offer unparalleled flexibility, scalability, and ease of development, crucial for effectively utilizing cloud functionalities. Moving away from the lift-and-shift approach, cloud-Native apps allow businesses to avoid issues like limited scalability, security vulnerabilities, and cost inefficiency. But, to ensure proper implementation of cloud-native application architecture, one must partner with a professional cloud testing service provider, like Tx (TestingXperts). It will become a strategic asset for businesses to grow in the digital environment, facilitate faster time-to-market, and improve customer experience.
How can Tx Help with Cloud-Native App Testing?

Cloud-Native applications improve enterprises’ ability to reduce time-to-market and eliminate upfront costs. This has led to its rising popularity; however, certain challenges are related to data security, integration, application performance, and privacy. Tx can help you define an effective strategy to test the cloud so that you can address all the challenges and pitfalls. We bring domain expertise in various industry verticals and experience in other non-functional testing services. Partnering with us will facilitate you with the following perks:
• A global team of testing professionals with experience testing large and complex cloud implementations.
• A pool of skilled CEHs (Certified Ethical Hackers) testing in accordance with international standards, including OWASP, OSSTMM, PCI-DSS, HIPAA, SOX, WAHH, etc.
• An extensive performance testing resource pool with expertise in proprietary, open source (e.g., JMeter) and third-party tools (LoadRunner, VSTS, LoadComplete, etc.).
• Tx-Automate, our ready-to-deploy and best-in-industry automation framework, for quicker test automation. It can easily integrate with cloud services like BrowserStack, LambdaTest, and with CI/CD processes using Jenkins, Azure pipelines.
• Expertise in test automation (e.g., UFT, Selenium, TestComplete, Coded UI, etc.).
To know more, contact our QA experts now.
Discover more
Get in Touch
Stay Updated
Subscribe for more info