Internet of Things (IoT) refers to the connection of physical objects or devices known as ‘Things’ with sensors, software, applications, servers, etc., interconnected through the internet. It allows the exchange of data across devices and sensors and enables devices to interact, collaborate, and learn from each other’s experiences, just like humans. IoT has brought a new wave of connectivity and is changing how businesses interact with their customers and how today’s customers engage with so many smart IoT products.
Content
1. IoT Apps in Insurance – A market outlook
2. Some Important Use Cases of IoT in Insurance
3. Significance of IoT apps in the Insurance
4. An Overview of IoT Testing
5. What is the importance of IoT testing for Insurance?
6. Various Types of IoT Testing Insurance Companies Should Leverage?
7. Conclusion
With billions of IoT devices and numerous IoT apps today, these apps play a significant role in easing human lives by bridging the physical and digital gap. There is much prominence of these IoT apps across all industries in the form of smart homes, connected cars, connected healthcare, smart wearables, smart real estate, smart insurance products, etc. But, the importance of IoT in the insurance sector has been more dominant today with the pandemic all around. Some of the most common insurance types include home insurance, health insurance, automotive insurance, etc. The significance of IoT apps in insurance continues to impact customers in a significant way and easing lives for customers in many ways.
IoT Apps in Insurance – A market outlook

According to Mordor Intelligence, the global IoT market is expected to reach a value of USD 1,386.06 billion by 2026 from USD 761.4 billion in 2020 at a CAGR of 10.53% during the forecast period 2021-2026.
According to MarketsandMarkets, The global IoT insurance market is expected to be worth USD 42.76 billion by 2022, growing at a CAGR of 65.89% during the forecast period (2016-2022.)
McKinsey’s Global Institute predicts that IoT will have an economic impact of between $4 trillion and $11 trillion by 2025.
According to Microsoft’s IoT Signals Report 2020, COVID-19 has accelerated the IoT adoption rate. One in three decision-makers states their organizations will increase investment in IoT due to COVID-19, while another 41% say they will maintain the same level of commitment.
Some Important Use Cases of IoT in Insurance
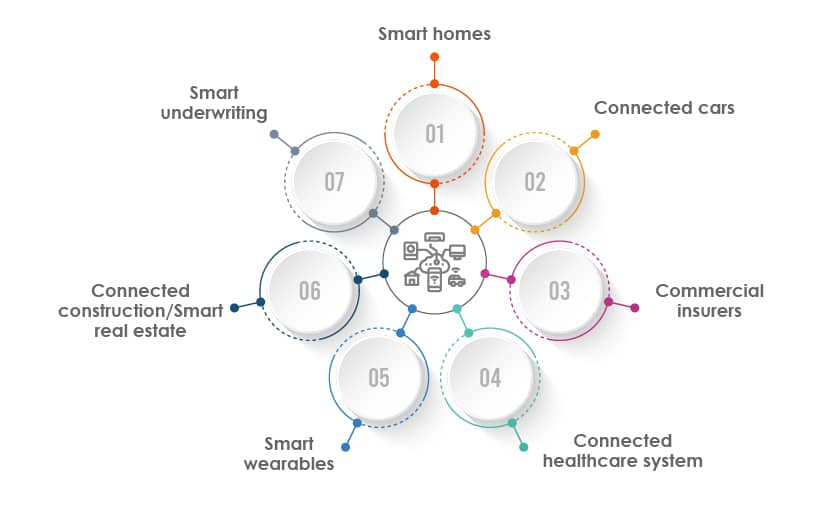
Smart homes:
There are various IoT devices such as smoke detectors, leak detectors, smart locks, air conditioners, etc., that users can control via IoT-connected apps. These IoT-enabled apps alert users in case of emergencies and help them take safety measures. Moreover, these IoT apps considerably reduce the chances of any probable disasters at homes and duly help reduce home insurance claims to a certain extent.
Connected cars:
Today, cars are getting connected with IoT apps via Telematics. Telematics devices collect data from within the vehicle and send it to the IoT cloud. This data is then pushed to the telematics applications, where stakeholders analyze it to make informed decisions. In case of accidents or mishappenings, an automatic notification is sent to the insurers, which results in faster processing of the insurance claims.
Commercial insurers:
With the help of IoT devices, apps, and sensors embedded in industrial units, commercial insurers adopt a dynamic rating model that enables risk-based pricing for the customers. Real-time data availability enabled by IoT apps helps insurers to manage risk and minimize losses significantly.
Connected healthcare system:
Connected healthcare systems have enabled interactions between healthcare systems, IoT apps, wearables, and healthcare professionals. Some IoT solutions track and monitor people’s heart rate, step counts, blood pressure, etc., in real-time and enable better healthcare services. Health insurers leverage this data to provide customized discounts and offer to customers.
Smart wearables:
Smart wearables such as Fitbit, Fitband, etc., and some other smart health apps such as Google fit, Strava, Sports tracker, etc., help track and monitor the individual’s health in an easy and innovative Insurers track this real-time data to customize insurance policies and offer discounts to individuals who follow a healthy lifestyle.
Connected construction/Smart real estate:
The real estate sector is highly competitive and involves some amount of risk. IoT technology connects job sites, machines, and workers and thus enables insurers to monitor the site virtually, assess land stability, and gather real-time data.
Smart underwriting:
Traditionally, insurance agents had to collect and rely on information provided by the applicants. With the advent of IoT apps in the Insurance sector, the underwriting process has become more efficient and faster. Insurers can create a better and precise client portfolio, assess the risks beforehand, reduce losses and build better relations with policyholders.
Significance of IoT apps in the Insurance
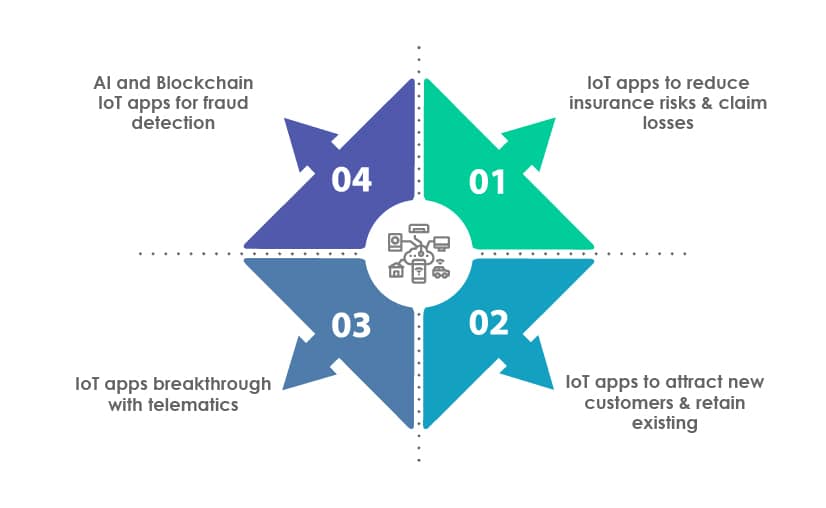
IoT apps are changing the insurance industry dynamics significantly in the following ways:
IoT apps to reduce insurance risks & claim losses:
IoT apps help insurers gather and analyze real-time customer data to provide better insurance policies, assess risks in advance, reduce chances of unnecessary claim requests, etc. It also helps to increase the overall profitability of insurance companies. According to a Forbes article, IoT could help insurers cut the cost of the claims process by 30% and lower premiums for consumers.
Let us see how IoT apps are leveraged across the sectors of healthcare, car, and home insurance:
Health insurance –
With the help of IoT apps, insurers now have access to better customer data which they can use to provide better insurance policies.
Health insurance providers can gather insured person’s health data to provide several types of discounts, such as special discounts for non-smokers, women, or unique plans for family or partners.
Car insurance –
With the help of IoT apps, various data points such as credit score, car location, car type, miles driven per year, age, gender, etc., are readily available to insurers.
Insurers leverage this data to offer better pricing models, offers, and discounts to responsible drivers and customers.
Real-time IoT data helps insurers to alert and assist drivers, thereby reducing the chances of unnecessary claims. In unfortunate cases, such as fatal accidents, an automatic notification is routed by IoT sensors to insurers which helps to quicken claims processing.
Home insurance –
Home insurers can gather real-time data via IoT apps and alert the homeowners and residents about the accident, such as any gas leak, water leakage, fire, smoke, robbery, etc.
IoT apps to attract new customers & retain existing ones:
The integration of IoT technology in the insurance sector has inevitably changed the insurance sector dynamics. With the help of IoT-enabled apps, insurers can now attract new customers and retain the existing ones. Certain IoT apps are linked to IoT sensors embedded in automobiles, and the respective app is installed in the vehicle owner’s smartphones. These sensors sense the collision, track the vehicle speed and alert the user by placing a call to the user to check if any assistance is required. If the user does not answer the phone call, the IoT app automatically sets an emergency call along with the vehicle’s location.
IoT apps breakthrough with telematics:
Telematics devices and apps help track and monitor connected cars’ activity. These telematics IoT apps can track the car and gather various data points such as the total number of miles covered, car health, car present value, etc. This way, IoT apps help insurers tailor policies according to the usage and age of the vehicle. Another way is the Usage-Based Insurance (UBI) model using which insurance companies judge the user behaviour based on the usage data collected via IoT apps. This saves customers from high-premium charges, expensive annual plans and also benefits insurance companies with quicker processes.
AI and Blockchain IoT apps for fraud detection:
According to Globe Newswire, the global insurance fraud detection market size is expected to grow from USD 2,518 million in 2019 to USD 7,928 million by 2024, at a CAGR of 25.8% from 2019 to 2024. There are various types of insurance frauds, such as payment fraud, invoice fraud, fraudulent claims, etc.
The AI and Blockchain IoT apps contain Customer Service Points (CSPs) that gather and analyze real-time data such as unexpected high or low app usage, unexpected transactions, high activity of IoT app in a particular location, etc. These CSPs observe abnormalities and alert the insurers, thus saving insurance companies from any probable frauds.
As detailed above, all these Insurance-based IoT apps for health, automotive, home, etc., are expected to perform seamlessly and deliver a great User Experience (UX). Therefore, businesses should leverage IoT testing to get fully functional, robust, and seamless IoT apps that are bound to deliver great UX.
An Overview of IoT Testing

IoT testing is a software testing type performed on IoT ecosystems (apps, devices, phones) to ensure their usability, security, connectivity, etc. Since IoT is the connection of several devices, it becomes difficult to find where the issue originates. Thus, IoT testing ensures that the IoT apps meet expected quality and performance standards for enabling a great UX. This testing method helps identify and rectify bugs in the IoT apps and improves IoT apps’ quality.
What is the importance of IoT testing for Insurance?
1. Delivers seamless app performance:
The insurance IoT apps are data-driven and work in real-time. Insurance service providers should ensure that IoT apps should perform seamlessly under all conditions. Thus, these seamless IoT apps help insurers reduce paperwork and make them move through the claim process quickly and easily.
2. Helps to manage data complexities:
IoT sensors generate a massive amount of data every millisecond. To achieve proper implementation of IoT, insurance companies need to ensure adequate storage and robust data management capabilities, which can only be achieved by adopting IoT testing of insurance apps.
3. Ensures safety and privacy of data:
The IoT apps are data-centric, and a vast amount of data is being stored and exchanged across devices via IoT apps. It is essential to ensure that no data leak or data loss happens via IoT apps. Also, to protect IoT apps and data from cyber threats, IoT testing is needed.
4. Provides real-time insights:
IoT apps capture, monitor, and analyze the user’s data such as health, behaviour, safety, etc., in real-time. It is essential to test these IoT apps to ensure no delay in tracking time and ensure these apps function effectively.
5. Validates compatibility across devices and OS:
Policyholders access insurance IoT apps on various devices and operating systems. To ensure seamless compatibility of IoT apps across all devices and OS, IoT testing is essential.
6. Improves scalability:
The basic concern of insurance providers is the safety of their customer data. With the help of effective IoT testing, insurers can place themselves as reliable and trustworthy insurance partners. This will improve the brand’s image and scalability of IoT apps in the insurance sector.
7. Helps insurers reach the market early:
IoT has made the world a better-connected place. Insurance service providers are leveraging IoT apps to connect with customers/prospects. It is essential to test IoT apps to ensure insurers reach the market early before competitors and deliver a great experience to customers
8. Saves cost:
End-to-end testing of IoT apps helps insurance providers increase these app’s efficiency. Automatic tracking, maintenance, and alert features of IoT apps help insurers to warn the policyholder well before any incident occurs. This way, insurers can save claim amounts and increase profitability.
9. Improves customer engagement:
IoT apps help insurers gain access to real-time customer data, which helps them provide better policies. This way, insurers design better customer engagement tactics and can also engage more customers.
Various Types of IoT Testing Insurance Companies Should Leverage?
1. Functionality testing:
This software testing method examines IoT sensor’s qualitative and quantitative deliverability and connected IoT apps. It ensures that the IoT apps perform seamlessly and work as expected under all conditions. Automating the functionality tests helps in saving time and ensures quality results.
2. Security testing:
Numerous users access the IoT apps, and a massive amount of data is exchanged across IoT devices and platforms via IoT apps. Thus, it is essential to look at various aspects of IoT apps such as data protection, encryption/decryption, device identity authentication, etc. Also, as there are a lot of interconnected devices and apps, the chances of cyber-threats and vulnerabilities are high, which again necessitates the need for IoT testing.
3. Usability testing:
Customers prefer IoT apps that are easy to use and perform seamlessly. As IoT technologies are being leveraged for smart homes, smart wearables, connected cars, telemedicine, etc., it is evident that only the best performing and easy to use IoT apps are successful. Thus, it is essential to conduct usability testing.
4. Performance testing:
This software testing type checks the performance of IoT apps in real-time. It ensures that the IoT apps perform seamlessly and matches various other performance factors such as network bandwidth, latency, packet loss, number of concurrent users, etc. Automating the performance testing of IoT apps helps in achieving effective testing results.
5. Exploratory testing:
This test is essential as it determines how IoT apps perform under real-world conditions. It helps QA teams evaluate how effectively IoT apps interact with IoT sensors and other interconnected devices.
6. Scalability testing:
This test involves the simulation of sensors by using various virtualization tools and technologies. It is vital to test the functional and non-functional aspects of the IoT apps to ensure the apps are scalable to accommodate future upgrades.
7. Connectivity testing:
This test aims to check the IoT device and application behaviour and performance when the network is subjected to a load or intermittent failure. It helps in building robust IoT apps. The apps are checked for various connectivity issues to ensure they perform well under all conditions
8. Compatibility testing:
This test validates that the IoT apps support and works seamlessly on various combinations of hardware, software, protocols, and operating systems
9. Regulatory testing:
This test ensures that the apps comply with privacy, government localization, accessibility, and other regulations.
Conclusion
IoT apps are connecting the world like never before. There has been a significant rise in the usage of IoT apps across the healthcare, insurance, and automobile sectors. The ability of IoT apps to track, monitor, and assess real-time data via IoT sensors and devices is immensely helping the insurance sector in offering better insurance services.
End-to-end testing of IoT apps with the latest automation testing techniques can help insurers deliver quality services and enhance UX. Enterprises must leverage IoT testing from a next-gen QA and software testing services provider to achieve robust, next-gen IoT apps.
Discover more
Get in Touch
Stay Updated
Subscribe for more info