Table of Contents
- Key Drivers of the Privacy Paradox in AI
- The Dual Role of AI – Innovation and a Guardian of Privacy
- Understanding the Data Privacy Paradox in Modern Enterprises
- Strategies for Balancing Innovation and Data Privacy
- The Role of Transparent Data Practices
- Overcoming Challenges in Adopting Privacy-Friendly AI Solutions
- How Privacy and AI Look in the Next Decade?
- Conclusion
- How Tx Can help in Innovating without Invading
Did you know? Nearly 84% of consumers are more loyal to companies with strong data privacy practices, yet 68% admit to being wary of how their data is used by AI systems.
These numbers highlight the critical juncture where innovation and privacy collide—a phenomenon we call the privacy paradox. Organizations are increasingly reliant on artificial intelligence to drive innovation, yet their customers demand transparency and control over personal data. This paradox challenges decision-makers to rethink their approach to AI-powered solutions.
Why Data Privacy Matters in AI
Enterprises are increasingly governed by AI algorithms thus data privacy is no longer just an ethical issue but a business imperative. Breaches can result in hefty fines, reputational damage, and loss of consumer trust. CTOs must ensure their AI systems comply with global regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, and CCPA while embedding ethical practices into their design and development processes.
Key Drivers of the Privacy Paradox in AI
- Convenience: Users often trade privacy for seamless services, such as personalized recommendations or real-time navigation.
- Personalization: Tailored content and experiences drive higher engagement but require substantial data inputs.
- Transparency: A lack of clarity on how data is collected, stored, and used exacerbates the paradox. Educating users on these processes can mitigate concerns.
The Dual Role of AI – Innovation and a Guardian of Privacy
Artificial Intelligence has reevaluated business landscapes—accelerating decision-making, personalizing customer experiences, and undo insights from complex datasets. However, the same capabilities that fuel innovation can also lead to unintended consequences, such as data breaches or the erosion of consumer trust.
To truly utilize AI, CTOs and other leaders must ensure their systems respect privacy by design, aligning technological advancements with ethical data practices.
Understanding the Data Privacy Paradox in Modern Enterprises
The data privacy paradox emerges from the conflicting needs of businesses and consumers:
- Businesses: Demand for vast datasets to train AI models and drive personalized innovation.
- Consumers: Increased skepticism and demand for transparency about how their data is used.
This dichotomy creates a trust gap, where organizations face mounting pressure to innovate responsibly while protecting sensitive information.
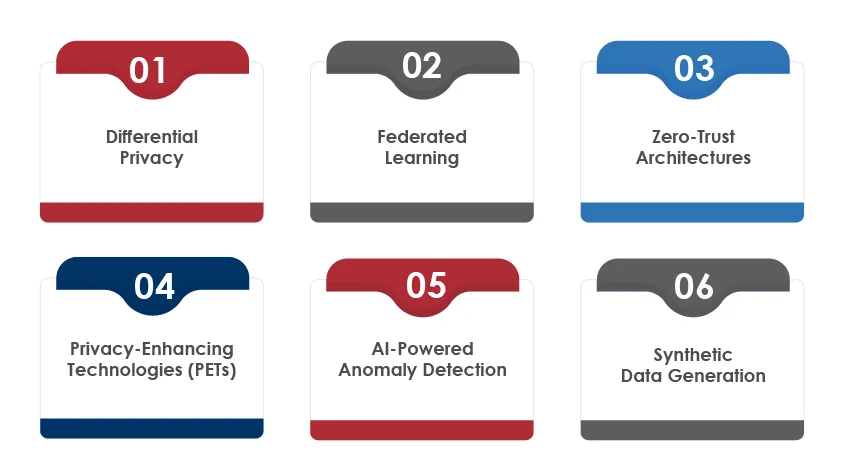
Strategies for Balancing Innovation and Data Privacy
Differential Privacy:
Adds statistical noise to data sets, preserving individual anonymity while maintaining analytical accuracy. This approach allows companies to extract meaningful insights without exposing personal details, making it ideal for sensitive industries like healthcare and finance.
Federated Learning:
Processes data locally on user devices, ensuring that raw data never leaves its source. By enabling collaborative model training across decentralized data, federated learning offers robust privacy protection while maintaining AI’s learning capabilities.
Zero-Trust Architectures:
Assumes no implicit trust and requires verification at every stage of data handling. This framework ensures that every interaction, whether internal or external, adheres to stringent security protocols.
Privacy-Enhancing Technologies (PETs):
Tools like homomorphic encryption and secure multi-party computation enable computations on encrypted data without exposing sensitive information. These technologies are pivotal for maintaining privacy in data-intensive AI operations.
AI-Powered Anomaly Detection:
Monitors data flows in real time to identify unusual activities that might indicate potential breaches. This proactive approach strengthens security by addressing threats before they escalate.
Synthetic Data Generation:
Creates artificial data sets that mimic real-world data without exposing personal information. Synthetic data allows AI models to train effectively while eliminating privacy concerns.
The Role of Transparent Data Practices
Transparency builds trust. Businesses must clearly communicate:
- What data is collected.
- How it’s used.
- Steps taken to protect it.
Integrating explainable AI (XAI) ensures that decisions made by AI models are interpretable, further reducing consumer skepticism.
Overcoming Challenges in Adopting Privacy-Friendly AI Solutions
1. High Implementation Costs
Privacy-preserving technologies often require significant upfront investment. However, the long-term benefits—customer loyalty, reduced compliance risks, and improved security—far outweigh the initial costs.
2. Regulatory Complexity
Navigating global data privacy laws like GDPR, HIPAA, or CCPA can be daunting. AI systems must be designed to adapt to these evolving requirements.
3. Organizational Resistance
Integrating new technologies often meets resistance. Leaders must foster a culture of innovation by demonstrating how privacy-conscious AI aligns with organizational goals.
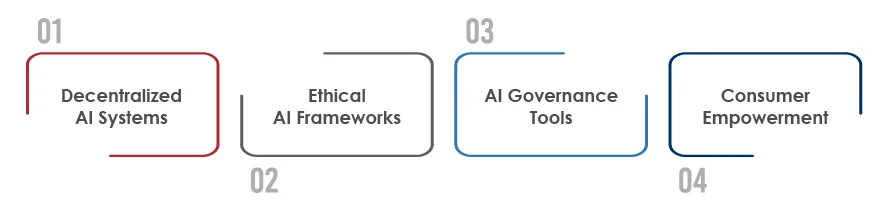
How Privacy and AI Look in the Next Decade?
- Decentralized AI Systems: Greater reliance on edge computing to process data locally.
- Ethical AI Frameworks: Development of globally accepted ethical standards for AI.
- AI Governance Tools: Adoption of tools to monitor AI’s compliance with privacy regulations.
- Consumer Empowerment: Enhanced mechanisms allowing users to control their data.
Conclusion
The Privacy Paradox is not an insurmountable challenge; it’s an opportunity to lead responsibly in a data-driven era. By adopting privacy-conscious AI strategies, businesses can achieve a competitive edge, develop consumer trust, and stay compliant in an increasingly regulated landscape.
For businesses, the time to act is now. Embrace AI solutions that innovate without invading and position your organization as a leader in ethical innovation.
How Tx Can help in Innovating without Invading
At Tx, we understand the intricate balance between driving innovation and safeguarding data. Our team of experts excel in:
- Designing AI systems that adhere to global privacy regulations.
- Implementing cutting-edge privacy-preserving technologies.
- Offering seamless integration of legacy systems with modern, secure architectures.
With Tx, you gain a partner committed to helping you navigate the privacy paradox, ensuring your AI initiatives inspire trust and drive results.
Discover more
Get in Touch
Stay Updated
Subscribe for more info